# Network
# Components in Network
- End devices (hosts): phone, tv, printer, ...
- Media: line, cables, ...
- Protocol
![]()
# Data Network
# Categories by Geo
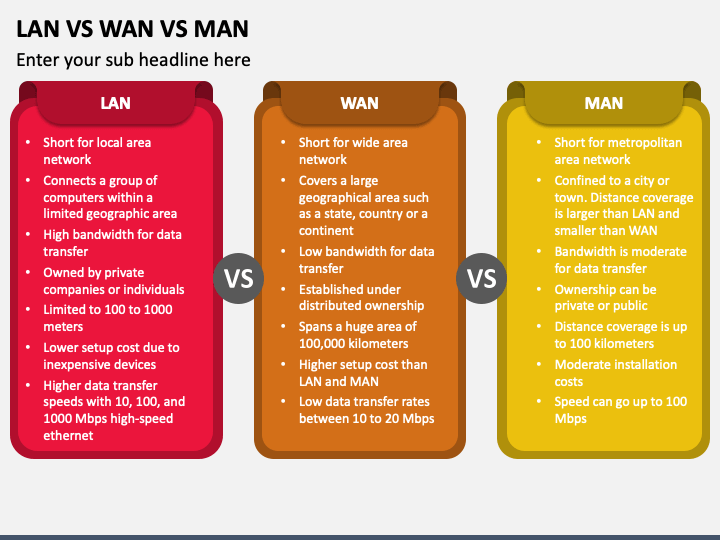
- LAN: Local Area Network
- WAN: Wide Area Network
- MAN: Metropolitan Area Network
- GAN: Global Area Network (continents connection)
- SAN: Storage Area Network (peformance + Availability + Scalability)
- VPN: Virtual Private Network
| Param | LAN | WAN |
|---|---|---|
| Speed | high, upto 1-10 Gbps | much lower, generally 100 mbps |
| Congestion | Less congested | More congested |
| Components | using the layer 1/2 devices like hubs, swiches, brigdes & layer 3 devices like Core/Layer 3 switch | using the layers 3 devices Routers & Multi-layer Switches |
| Ownership & management | owned, operated, managed & monitored by a customer | by multiple Service providers |
| Security | More secured | Less secured |
| Technologies | Ethernet & Token Rings | MPLS, ATM, Frame replay & ISDN, ... |
| Cost | Less expensive | More expensive |
| Physical layer connectivity | Generally Copper & Fiber medium. Multimode Fider is preferred. | Fiber medium. Single mode Fiber is preferred |
# WAN vs LAN vs PAN vs MAN

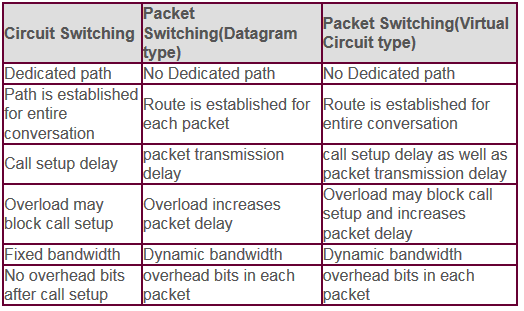
# Categories by switching
# VPN (Virtual Private Network)
Connect objects
- Headquarter
- Branch
- Home user
- Mobile user (laptop, mobile)
https://www.slideshare.net/OECLIBOdishaElectron/virtual-private-networks-vpn-ppt
Types :
- Network to network (Site to Site)
- Intranet: network same company
- Extranet: network between multi companies
- User to Network (Remote-Access VPN) (POP)
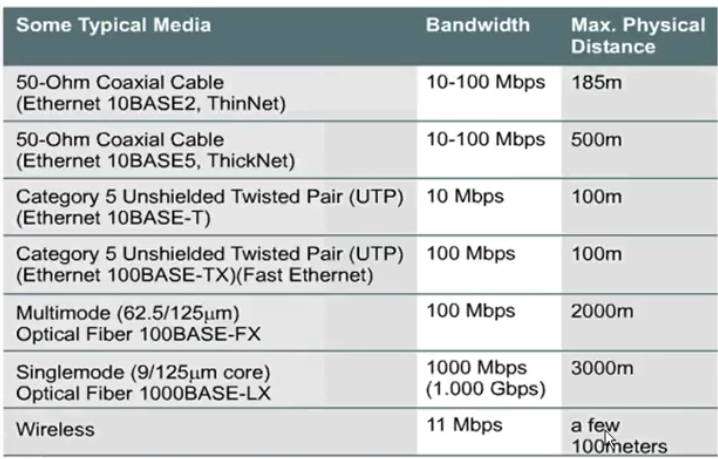
# Media
LAN Media
- đồng trục
- xoắn đôi
- cáp quang
- vô tuyến
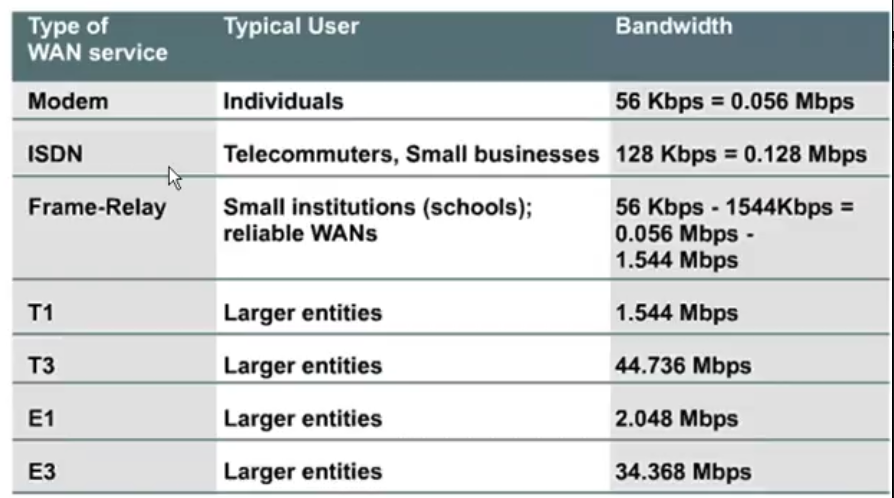
WAN Media
- modem (dial-up)
- public data network service (VPN, Frame-relay)
- đường thuê bao dùng riêng (Leasedline based on bandwidth)
# Models
Communication Process
Source Address ----- Protocol on Media ----- Destination Address
- Addresses: who are the source & destination of a communication process
- Media: where is the communication take place
- Protocols: set of rules how to make communication on a network
# Protocols
# Common protocols


# Common servers

# Vokas
- Round-trip time (RTT)
- Network Interface Card (NIC)
- 1 B (Byte) = 8 bit (b)
- 1024 B = 1 KB
- Bandwith (bps - bit per second)
- Through put <= Bandwidth ( P (throughput) = S (size of file) / T (time to download) )
- LLC - Logical Link Control
- MAC - Media Access Control
# Tools
- Decimal to Binary converter (opens new window)
- Visual Subnet Calculator (opens new window)
- CIDR (opens new window)
# Refs
https://viblo.asia/p/so-sanh-chi-tiet-tcp-va-udp-tai-sao-udp-lai-nhanh-hon-tcp-zOQJw05xLMP