# Devices
https://www.geeksforgeeks.org/network-devices-hub-repeater-bridge-switch-router-gateways/
# Repeater
- regenerate the signal over the same network before the signal becomes too weak or corrupted to extend the length to which the signal can be transmitted over the same network
# Hub
- A hub is a basically multi-port repeater
- A hub connects multiple wires coming from different branches
# Bridge
- Data Link (Layer 2) device
- A bridge is a repeater, with add on filtering content by reading the MAC addresses of the source and destination.
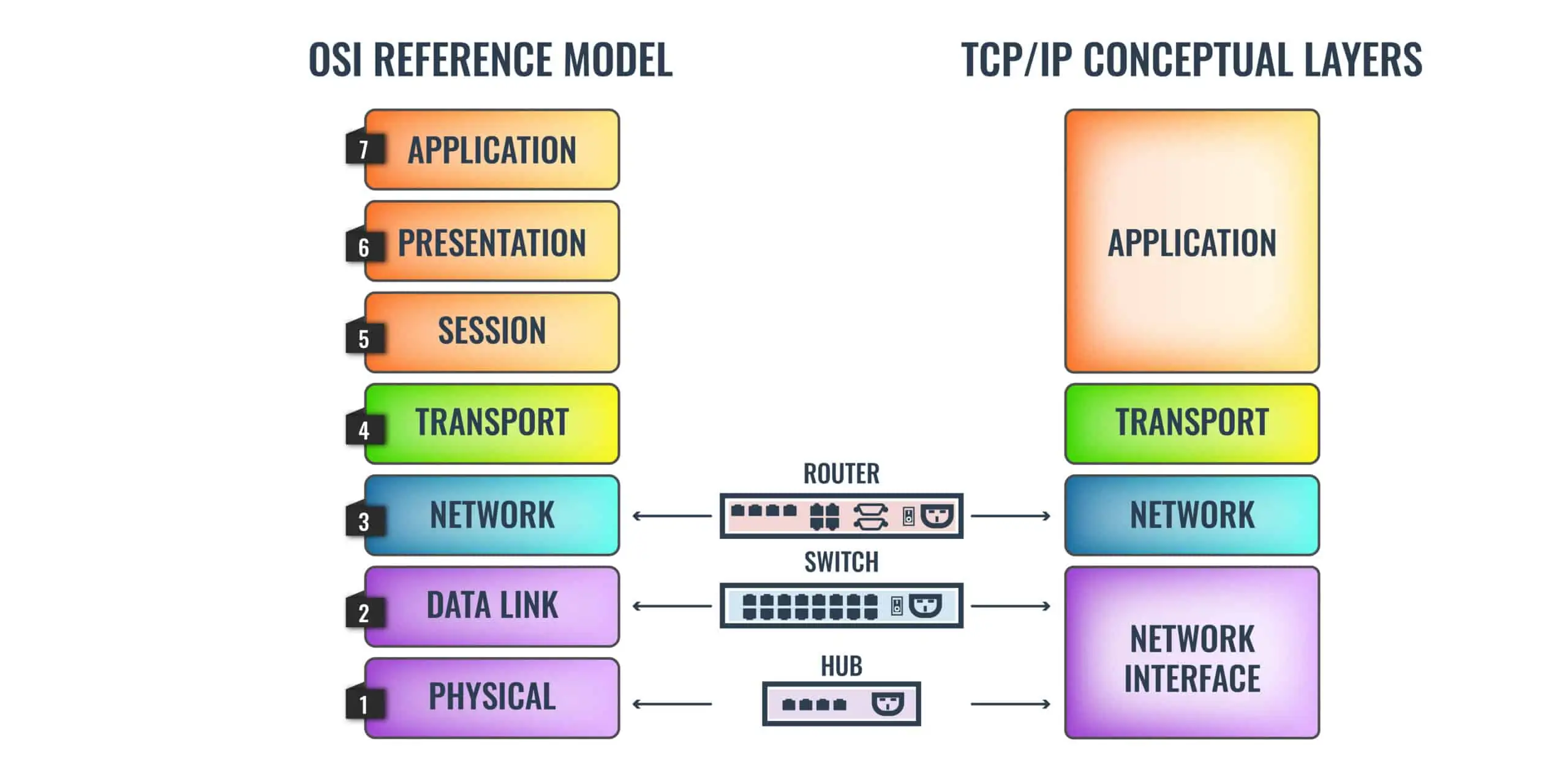
# Routers and the OSI Layers
# Switch
- Has no IP address, only MAC address
# NIC (network interface card)
- NIC card is a layer 2 device
- network interface card is a network adapter that is used to connect the computer to the network.
- It is installed in the computer to establish a LAN.
# MAC address
- MAC (Media Access Control) address = unique identifier assigned to a network interface card (NIC).
- Usually hard-coded by the manufacturer (burned into hardware).
- Format:
00:1A:2B:3C:4D:5E(48-bit).
# Can MAC change?
Permanent (factory-assigned) MAC
- Most NICs come with a fixed MAC, usually not changing.
- This is called the hardware or burned-in address.
Temporary / Software-assigned MAC
- Operating systems and some applications allow MAC spoofing.
- You can manually change the MAC for a NIC using software or OS commands.
- Example:
- Linux:
sudo ip link set dev eth0 address 02:11:22:33:44:55 - Windows: Change via Network Adapter → Advanced → Network Address
- Linux:
Randomized / privacy MAC
- Modern OSs (iOS, Android, Windows 10+) can randomize MAC addresses for Wi-Fi connections to prevent tracking.
- Example: When connecting to public Wi-Fi, your device may use a temporary randomized MAC instead of the factory MAC.
# Hub vs Switch vs Router
| Features | Hub | Switch | Router |
|---|---|---|---|
| OSI layer | 1 | 2 | 3 |
| type | broadcast device | multicast device | routing device |
| connect devices | same network | same network | different networks |
| send data at same time | only 1 device | multiple devices | multiple devices |
| stored info | not any info | MAC addresses | IP addresses |
# Router vs Switch
| Features | Router | Switch |
|---|---|---|
| speed | slower | faster |
| ISO layer | layer 3 | layer 2 |
| addressing used | IP | MAC |
| broadcasts | Blocks | Forwards |
| security | high | lower |
# Router
- A router is a device like a switch that routes data packets based on their IP addresses.
- Routers connect 2 or more networks, each of which must have a unique network number in order for routing to be succesful
- Has many IPs, because has many NIC
- find the most efficient path for delivery of data on network
TIP
Routers primarily operate at Layer 3 (Network Layer) — that’s where IP routing happens.
BUT routers interact with all other layers because they must send, receive, manage, and secure traffic — and those functions live at other layers.
Example in Real Life
| Function | Example Protocol | Layer | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| Route exchange between ISPs | BGP | Layer 3 / 4 | Uses TCP port 179 |
| Dynamic routing inside company | OSPF | Layer 3 | IP protocol 89 |
| Local MAC resolution | ARP | Layer 2 | Maps IP to MAC |
| Diagnostic ping | ICMP | Layer 3 | Echo request/reply |
| Remote admin | SSH | Layer 7 (uses TCP 22) | Secure configuration access |
| Monitoring | SNMP | Layer 7 (uses UDP 161) | Collects router stats |
| VPN tunnel | IPSec / GRE | Layer 3 / 6 | Encrypts or encapsulates IP packets |
# Aws services
| Device. | Description | AWS Equivalent / Service |
|---|---|---|
| Router | Directs packets between networks (e.g., LAN ↔ Internet). | VPC Router (built-in to AWS VPC) |
| Switch | Connects multiple devices in the same network (Layer 2). | Virtual Switches inside EC2 hypervisors (not user-managed) |
| Firewall | Filters incoming/outgoing traffic based on security rules. | Security Groups, Network ACLs, AWS Network Firewall |
| Load Balancer | Distributes traffic across multiple servers. | Elastic Load Balancing (ALB, NLB, GLB) |
| NAT (Network Address Translation) | Allows private instances to access the internet using one public IP. | NAT Gateway, NAT Instance |
| Gateway | Connects networks using different protocols (e.g., VPC ↔ Internet or on-prem). | Internet Gateway, Virtual Private Gateway, Transit Gateway |
| DNS Server | Resolves domain names to IPs. | Amazon Route 53 |
| Proxy Server | Intermediary between client and destination for filtering/caching. | AWS CloudFront, AWS Global Accelerator, App Mesh |
| VPN Concentrator | Manages VPN tunnels for encrypted connections. | AWS Site-to-Site VPN, Client VPN |
| IDS/IPS (Intrusion Detection/Prevention System) | Detects or blocks malicious activity. | AWS GuardDuty, AWS Network Firewall (IPS) |
| Content Delivery Network (CDN) | Caches content closer to users for faster delivery. | Amazon CloudFront |