# Payment Service Providers (PSPs)
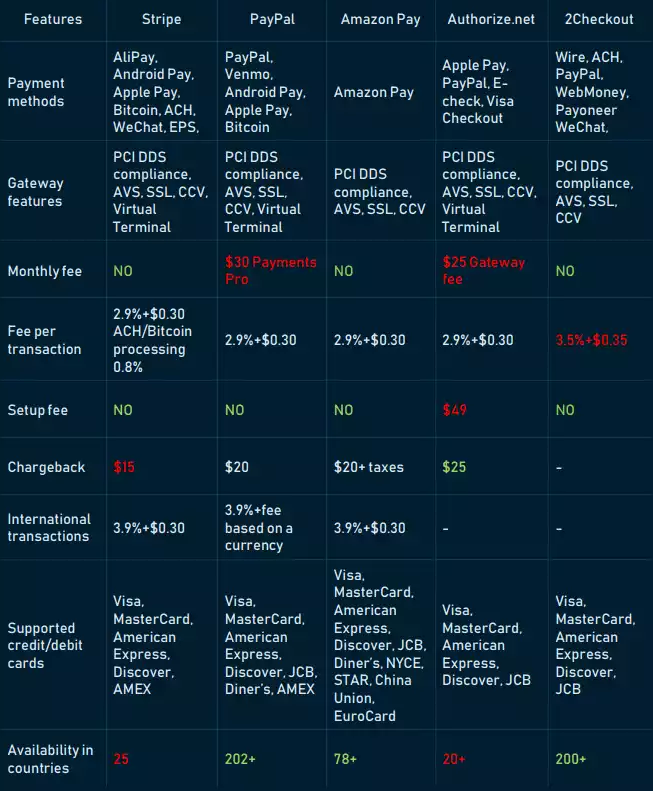
# Popular PSPs
# Types
# 1. Traditional Banks
- Role: Many banks offer payment processing services to their merchant customers, either directly or through partnerships with third-party PSPs.
- Advantages: Established trust, comprehensive financial services.
- Disadvantages: Potentially higher fees, slower onboarding process.
# 2. Independent PSPs
- Role: Standalone companies specializing in payment processing services.
- Advantages: Flexibility, advanced features, competitive pricing.
- Disadvantages: Might lack the comprehensive financial services of banks.
# 3. Payment Gateways
- Role: Focus solely on providing payment gateway services, enabling merchants to securely accept online payments.
- Advantages: Easy integration, wide range of payment options.
- Disadvantages: Limited to payment processing, additional services might be required.
# 4. Aggregators
- Role: Combine multiple payment methods and present them as a single solution to merchants.
- Advantages: Simplified integration, access to various payment options.
- Disadvantages: Potentially higher fees, less control over payment processing.
# 5. Merchant Acquirers
- Role: Handle the authorization and settlement of credit and debit card transactions.
- Advantages: Direct access to card networks, potential for lower fees.
- Disadvantages: Complex setup, higher operational costs.
# Additional Types**:
- Mobile Payment Processors: Specialize in processing payments made through mobile devices.
- E-wallet Providers: Offer digital wallet services for storing and transferring funds.
# Payment Processor vs. Payment Gateway
While both are essential components of electronic transactions, payment processors and payment gateways serve distinct roles.
# Payment Gateway
- The interface: A payment gateway is the online equivalent of a physical point-of-sale terminal.
- Collects information: It securely collects customer payment information (card number, expiration date, CVV).
- Transmits data: Encrypts and sends this information to the payment processor.
- Provides feedback: Communicates the transaction's approval or decline back to the merchant.
# Payment Processor
- The backend: Handles the complex process of routing and processing the transaction.
- Verifies information: Checks the validity of the payment information.
- Authorizes transaction: Communicates with the customer's bank to authorize the purchase.
- Transfers funds: Facilitates the transfer of funds from the customer's bank to the merchant's account.
- Fraud prevention: Implements security measures to protect against fraudulent transactions.
# Summarization
- Payment gateway: The customer-facing part of the transaction.
- Payment processor: The behind-the-scenes engine that makes it happen.
← Paypal notes Network →