# Obtaining IP / ARP / DHCP
# IP Address assignment
- MAC Address (6 bytes) : data link layer (L3)
- first 3 bytes: Organizational Unique Identifier
- last 3 bytes: Vendor Assigned (NIC Cards, Interfaces)
- IP Network (4 bytes): network layer (L2)

# Static addressing
...
# Dynamic addressing - DHCP
DHCP = Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol
defined range of IP addresses (scope) on A DHCP server
# Process
- Client Request : DHPC Discover / UDP Broadcast
- Server Response : DHPC Offer / UDP Broadcast
- IP Address
- Lease time
- DHCP Server IP
- Address
- Client Request : DHPC Request
- Server Response : DHPC Ack
- Gateway
- Ip of other servers
- ...
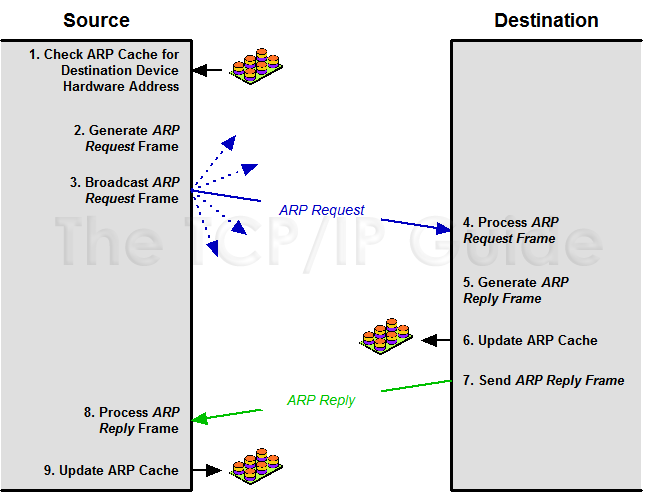
# Address Resolution Protocol (ARP)

- ARP enables a computer to find the MAC address of the computer that is associated with an IP address
- In order for devices to communicate, the sending devices need both IP addresses & the MAC addresses of the destination devices.
- When they try to communicate with devices whose IP addreses they know, they must determine the MAC addresses
- ARP table stores in RAM
Destination local
Find Device or IP Address using MAC Address (opens new window)