# Route 53
# What is DNS?
Domain Name System (DNS) which translates the human friendly hostnames into the machine IP addresses
E.g: www.google.com => 172.217.18.36
- DNS is the backbone of the Internet
- DNS uses hierarchical naming structure
# DNS Terms
- Domain Registrar: Amazon Route 53, GoDaddy, …
- DNS Records: A, AAAA, CNAME, NS, …
- Zone File: contains DNS records
- Name Server: resolves DNS queries (Authoritative or Non-Authoritative)
- Top Level Domain (TLD):
.com,.us,.in,.gov,.org, … - Second Level Domain (SLD):
amazon.com,google.com, …
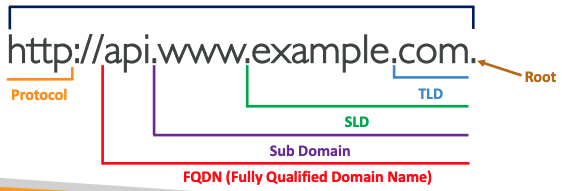
# How it works
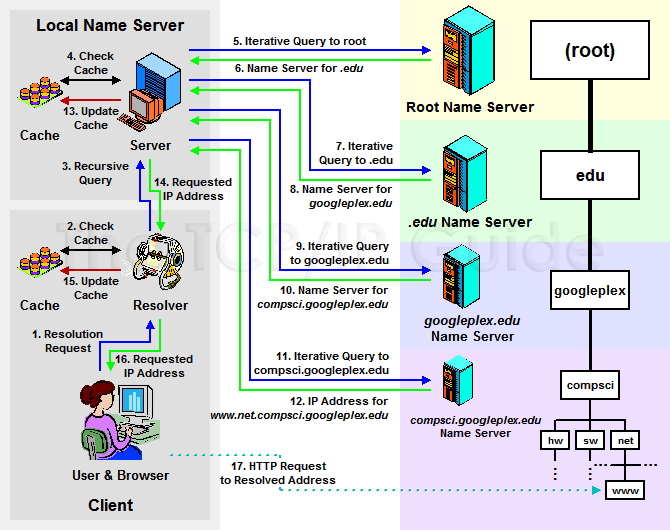
- Local DNS Server: Assigned and Managed by your company or assigned by your ISP dynamically
- Root DNS Server: Managed by ICANN
- TLD DNS Server (
.edu): Managed by IANA (Branch of ICANN) - SLD DNS Server (
googleplex.edu): Managed by Domain Registrar (e.g., Amazon Registrar, Inc.)
# Amazon Route 53
- A highly available, scalable, fully managed and Authoritative DNS
- Authoritative = the customer (you) can update the DNS records
- Route 53 is also a Domain Registrar
- Ability to check the health of your resources
- The only AWS service which provides 100% availability SLA
- Why Route 53? 53 is a reference to the traditional DNS port
# Records
- How you want to route traffic for a domain
- Each record contains:
- Domain/subdomain Name – e.g., example.com
- Record Type – e.g., A or AAAA
- Value – e.g., 12.34.56.78
- Routing Policy – how Route 53 responds to queries
- TTL – amount of time the record cached at DNS Resolvers
- Route 53 supports the following DNS record types:
- (must know) A / AAAA / CNAME / NS
- (advanced) CAA / DS / MX / NAPTR / PTR / SOA / TXT / SPF / SRV
| Types | Desc |
|---|---|
| A | maps a hostname to IPv4 |
| AAAA | maps a hostname to IPv6 |
| CNAME | maps a hostname to another hostname - The target is a domain name which must have an A or AAAA record - Can’t create a CNAME record for the top node of a DNS namespace (Zone Apex). E.g: can't create for example.com but can create www.example.com |
| NS | Name Servers for the Hosted Zone - Control how traffic is routed for a domain |
# Records TTL (Time To Live)
- High TTL – e.g., 24 hr
- Less traffic on Route 53
- Possibly outdated records
- Low TTL – e.g., 60 sec.
- More traffic on Route 53 ($$)
- Records are outdated for less time
- Easy to change records
- Except for Alias records, TTL is mandatory for each DNS record
# CNAME vs Alias
- AWS Resources (Load Balancer, CloudFront...) expose an AWS hostname:
lb1-1234.us-east-2.elb.amazonaws.comand you wantmyapp.mydomain.com
- CNAME:
- Points a hostname to any other hostname. (
app.mydomain.com=>blabla.anything.com) - ONLY FOR NON ROOT DOMAIN (aka.
something.mydomain.com)
- Points a hostname to any other hostname. (
- Alias:
- Points a hostname to an AWS Resource (
app.mydomain.com=>blabla.amazonaws.com) - Works for ROOT DOMAIN and NON ROOT DOMAIN (aka
mydomain.com) - Free of charge
- Native health check
- Points a hostname to an AWS Resource (
# Alias Records
- Maps a hostname to an AWS resource
- An extension to DNS functionality
- Automatically recognizes changes in the resource’s IP addresses
- Unlike CNAME, it can be used for the top node of a DNS namespace (Zone Apex), e.g.:
example.com - Alias Record is always of type A/AAAA for AWS resources (IPv4 / IPv6)
- You can’t set the TTL
| Record Name | Type | Value |
|---|---|---|
example.com | A | MyALB-123456789.useast1.elb.amazonaws.com |
Alias Records Targets
- Elastic Load Balancers
- CloudFront Distributions
- API Gateway
- Elastic Beanstalk environments
- S3 Websites
- VPC Interface Endpoints
- Global Accelerator accelerator
- Route 53 record in the same hosted zone
- You cannot set an ALIAS record for an EC2 DNS name
# Hosted Zones
- A container for records that define how to route traffic to a domain and its subdomains
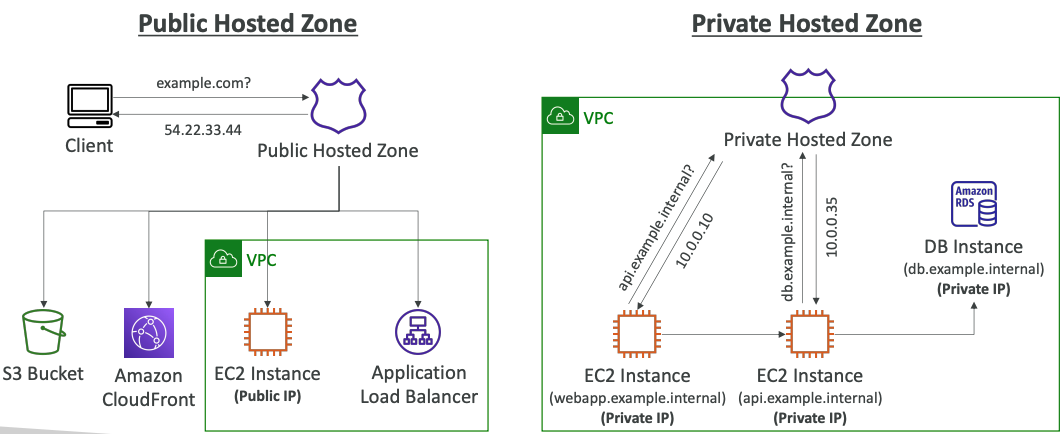
- Public Hosted Zones – contains records that specify how to route traffic on the Internet (public domain names)
application1.mypublicdomain.com - Private Hosted Zones – contain records that specify how you route
traffic within one or more VPCs (private domain names)
application1.company.internal - You pay $0.50 per month per hosted zone
# Public vs. Private Hosted Zones
# Routing Policies
- Define how Route 53 responds to DNS queries
- Don’t get confused by the word “Routing”
- It’s not the same as Load balancer routing which routes the traffic
- DNS does not route any traffic, it only responds to the DNS queries
- Route 53 Supports the following Routing Policies
- Simple
- Weighted
- Failover
- Latency based
- Geolocation
- Multi-Value Answer
- Geoproximity (using Route 53 Traffic Flow feature)
# Simple
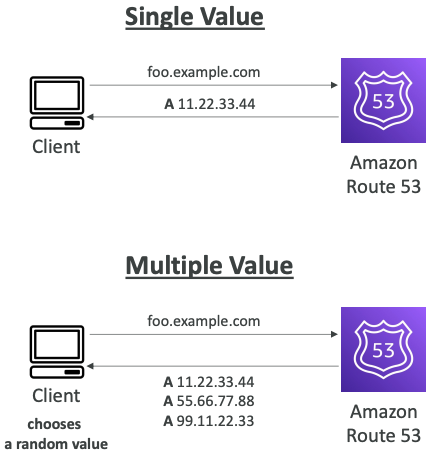
- Typically, route traffic to a single resource
- Can specify multiple values in the same record
- If multiple values are returned, a random one is chosen by the client
- When Alias enabled, specify only one AWS resource
- Can’t be associated with Health Checks
# Weighted
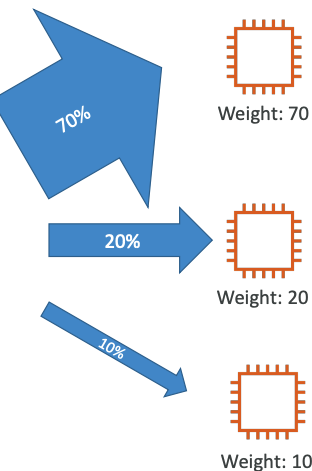
- Control the % of the requests that go to each specific resource
- Assign each record a relative weight:
- traffic (%) = Weight for a specific record / Sum of all the weights for all records
Weights don’t need to sum up to 100
- DNS records must have the same name and type
- Can be associated with Health Checks
- Use cases: load balancing between regions, testing new application versions…
- Assign a weight of 0 to a record to stop sending traffic to a resource
- If all records have weight of 0, then all records will be returned equally
# Latency-based
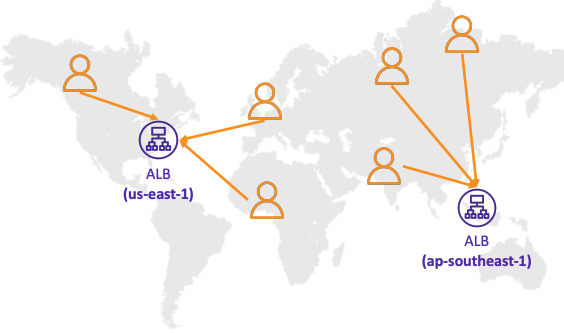
- Redirect to the resource that has the least latency close to us
- Super helpful when latency for users is a priority
- Latency is based on traffic between users and AWS Regions
- Germany users may be directed to the US (if that’s the lowest latency)
- Can be associated with Health Checks (has a failover capability)
# Failover (Active-Passive)
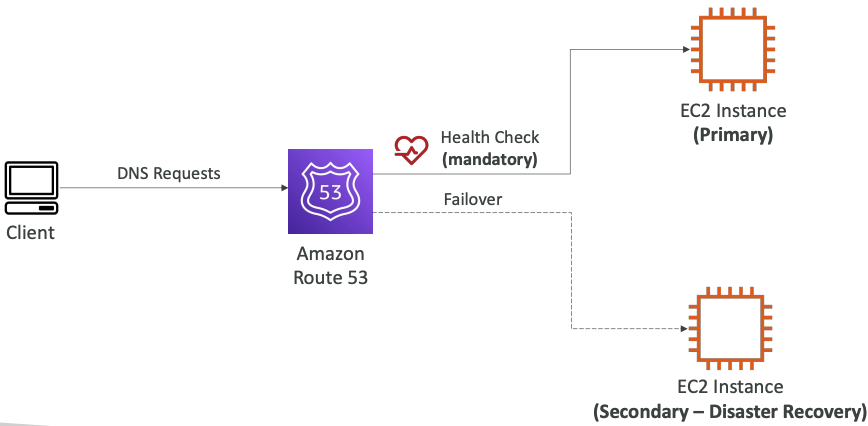
Primary must use with health check
# Geolocation
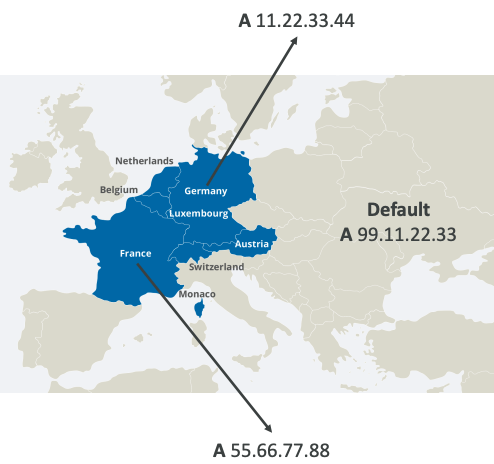
- Different from Latency-based!
- This routing is based on user location
- Specify location by Continent, Country or by US State (if there’s overlapping, most precise location selected)
- Should create a “Default” record (in case there’s no match on location)
- Use cases: website localization, restrict content distribution, load balancing, …
- Can be associated with Health Checks
# Geoproximity
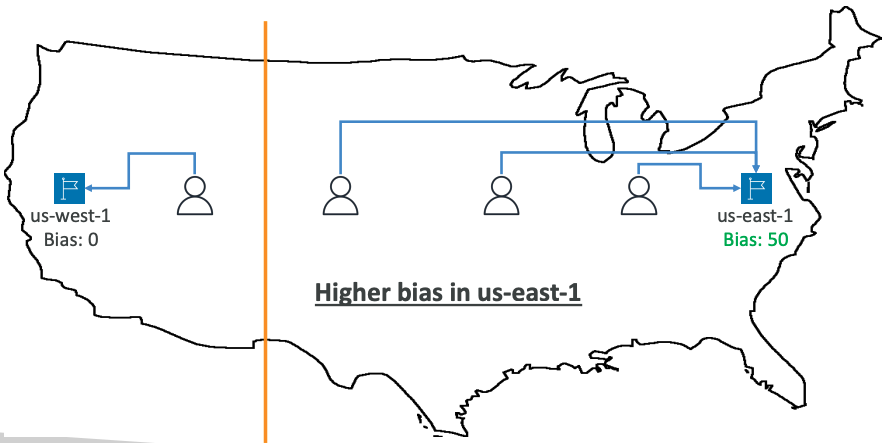
- Route traffic to your resources based on the geographic location of users and resources
- Ability to shift more traffic to resources based on the defined bias
- To change the size of the geographic region, specify bias values:
- To expand (
1 to 99) – more traffic to the resource - To shrink (
-1 To -99) – less traffic to the resource
- To expand (
- Resources can be:
- AWS resources (specify AWS region)
- Non-AWS resources (specify Latitude and Longitude)
- You must use Route 53 Traffic Flow to use this feature
# IP-based Routing

- Routing is based on clients’ IP addresses
- You provide a list of CIDRs for your clients and the corresponding endpoints/locations (user-IP-to-endpoint mappings)
- Use cases: Optimize performance, reduce network costs…
- Example: route end users from a particular ISP to a specific endpoint
# Multi-Value
- Use when routing traffic to multiple resources
- Route 53 return multiple values/resources
- Can be associated with Health Checks (return only values for healthy resources)
- Up to 8 healthy records are returned for each Multi-Value query
- Multi-Value is not a substitute for having an ELB
| Name | Type | Value | TTL | Set ID | Health Check |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| www.example.com | A Record | 192.0.2.2 | Web1 | A | |
| www.example.com | A Record | 198.51.100.2 | Web2 | B | |
| www.example.com | A Record | 203.0.113.2 | Web3 | C |
# Health checks
- HTTP Health Checks are only for public resources
- Health Check => Automated DNS Failover:
- Health checks that monitor an endpoint (application, server, other AWS resource)
- Health checks that monitor other health checks (Calculated Health Checks)
- Health checks that monitor CloudWatch Alarms (full control !!) – e.g., throttles of DynamoDB, alarms on RDS, custom metrics,… (helpful for private resources)
- Health Checks are integrated with CW metrics
# Monitor an Endpoint
- About 15 global health checkers will check the endpoint health
- Healthy/Unhealthy Threshold – 3 (default)
- Interval – 30 sec (can set to 10 sec – higher cost)
- Supported protocol: HTTP, HTTPS and TCP
- If
> 18%of health checkers report the endpoint is healthy, Route 53 considers it Healthy. Otherwise, it’s Unhealthy - Ability to choose which locations you want Route 53 to use
- Health Checks pass only when the endpoint responds with the 2xx and 3xx status codes
- Health Checks can be setup to pass / fail based on the text in the first 5120 bytes of the response
- Configure you router/firewall to allow incoming requests from Route 53 Health Checkers
# Calculated Health Checks
- Combine the results of multiple Health Checks (Children) into a single Health Check (Parent)
- You can use OR, AND, or NOT
- Can monitor up to 256 Child Health Checks
- Specify how many of the health checks need to pass to make the parent pass
- Usage: perform maintenance to your website without causing all health checks to fail
# Private Hosted Zones
- Route 53 health checkers are outside the VPC
- They can’t access private endpoints (private VPC or on-premises resource)
TIP
You can create a CloudWatch Metric and associate a CloudWatch Alarm, then create a Health Check that checks the alarm itself
# Domain Registar vs. DNS Service
- You buy or register your domain name with a Domain Registrar typically by paying annual charges (e.g., GoDaddy, Amazon Registrar Inc., …)
- The Domain Registrar usually provides you with a DNS service to manage your DNS records
- But you can use another DNS service to manage your DNS records
Example: purchase the domain from GoDaddy and use Route 53 to manage your DNS records
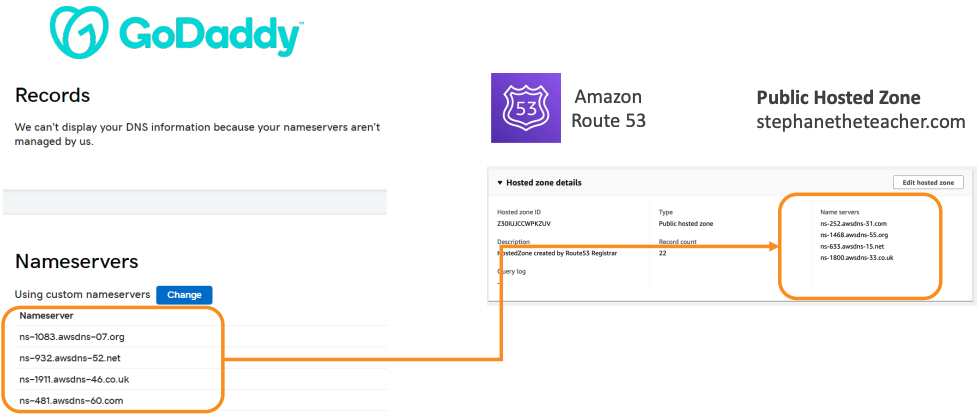
- If you buy your domain on a 3rd party registrar, you can still use Route 53 as the DNS Service provider
- Create a Hosted Zone in Route 53
- Update NS Records on 3rd party website to use Route 53 Name Servers
- Domain Registrar != DNS Service
- But every Domain Registrar usually comes with some DNS features