# Cloud Terms
# Cloud computing
the practice of using a network of remote servers hosted on the Internet to store, manage, and process data, rather than a local server or a personal computer.
| On-premise | Cloud Provider |
|---|---|
| You own the servers | Someone else owns the servers |
| You hire the IT people | Someone else hires the IT people |
| You pay or rent the real-estate | Someone else pays or rents the real-estate |
| You take all the risk | You are responsible for your configuring cloud services and code, someone else takes care of the rest. |
# Cloud Service Provider
- provides multiple Cloud Services e.g. tens to hundreds of services
- those Cloud Services can be chained together to create cloud architectures
- those Cloud Services are accessible via Single Unified API eg. AWS API
- those Cloud Services utilized metered billing based on usage e.g. per second, per hour
- those Cloud Services have rich monitoring built in eg. AWS Cloud Trail
- those Cloud Services have an Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS) offering
- Those Cloud Services offers automation via Infrastructure as Code (IaC)
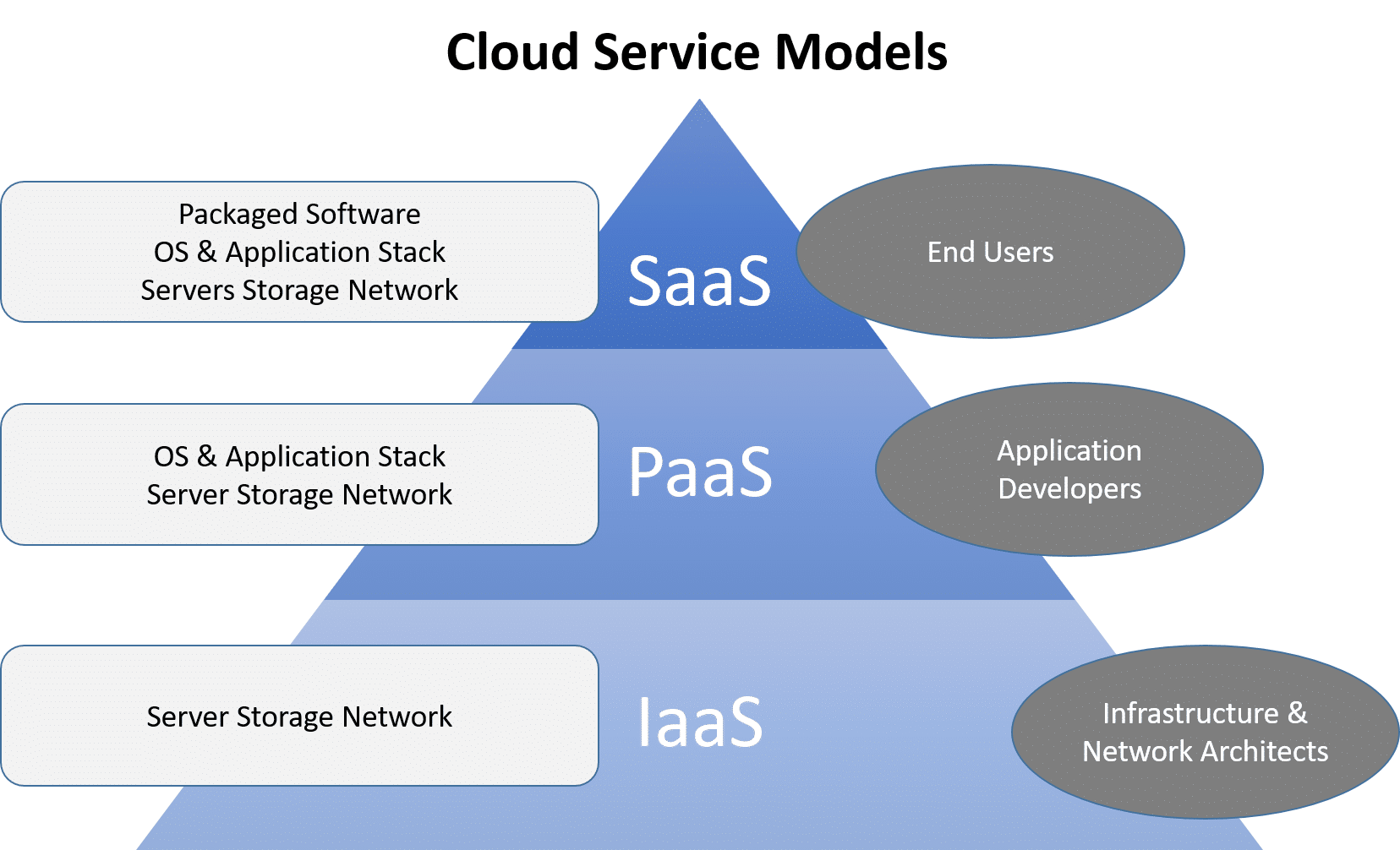
# Cloud Computing Models
# Cloud Computing Deployment Models
Public Cloud (Cloud-Native or Cloud First) Everything (the workload or project) is built on the SP
Private Cloud (On-Premise) Everything built on company's datacenters
Hybrid Using both On-Premise and A Cloud Service Provider
# Technology Overview
Cloud Service Provider (CSPs) that are Infrastructure as a Service (laas) will always have 4 core cloud service offerings:
- Compute
- Storage
- Database
- Networking & Content Delivery
# Landscape of CSPs
- Tier-1 (Top Tier) - Early to market, wide offering, strong synergies between services, well recognized in the industry
- AWS
- Microsoft Azure
- Google Cloud Platform (GCP)
- Alibaba Cloud
- Tier-2 (Mid Tier) - Backed by well-known tech companies, slow to innovate and turned to specialization.
- IBM Cloud
- Oracle Cloud
- Rackspace (OpenStack)
- Tier-3 (Light Tier) - Virtual Private Servers (VPS) turned to offer core laaS offering. Simple, cost-effective
- Vultr
- Digital Ocean
- Linode
# Evolution of Cloud Hosting
# Dedicated Server
- One physical machine dedicated to a single business.
- Runs a single web-app/site.
- Very Expensive, High Maintenance, High Security
# Virtual Private Server (VPS)
- One physical machine dedicated to a single business.
- The physical machine is virtualized into sub-machines
- Runs multiple web-apps/sites
- Better Utilization and Isolation of Resources
# Shared Hosting
- One physical machine, shared by hundred of businesses
- Relies on most tenants under-utilizing their resources.
- Very Cheap, Limited functionality, Poor Isolation
# Cloud Hosting
- Multiple physical machines that act as one system.
- The system is abstracted into multiple cloud services
- Flexible, Scalable, Secure, Cost-Effective, High Configurability
# Evolution of Computing
# Dedicated
- A physical server wholly utilized by a single customer
- You have to guess your capacity
- you'll overpay for an underutilized server
- You can't vertical scale, you need a manual migration
- Replacing a server is very difficult
- You are limited by your Host Operating System
- Multiple apps can result in conflicts in resource sharing
- You have a guarantee of security, privacy, and full utility of underlying resources
# Virtual Machines (VMs)
- You can run multiple Virtual Machines on one machine.
- Hypervisor is the software layer that lets you run the VMs
- A physical server shared by multiple customers
- You are to pay for a fraction of the server
- You'll overpay for an underutilized Virtual Machine
- You are limited by your Guest Operating System
- Multiple apps on a single Virtual Machine can result in conflicts in resource sharing
- Easy to export or import images for migration
- Easy to Vertical or Hortizonalty scale
# Containers
- Virtual Machine running multiple containers
- Docker Demon is the name of the software layer that lets you run multiple containers.
- You can maximize the utilize of the available capacity which is more cost-effective
- Your containers share the same underlying OS so containers are more efficient than multiple VMs
- Multiple apps can run side by side without being limited to the same OS requirements and will not cause conflicts during resource sharing
# Functions
- Are managed VMs running managed containers.
- Known as Serverless Compute
- You upload a piece of code, choose the amount of memory and duration.
- Only responsible for code and data, nothing else
- Very cost-effective, only pay for the time code is running, VMs only run when there is code to be executed
- Cold Starts is a side-effect of this setup