# Apache Cassandra
- Developed by Facebook in 2007. Gifted to Apache 2/2010
- NoSQL but has structure
- A database - column family
- Can use SQL to manipulate with data
- Peer to peer database, sharding, more nodes more performance
# Column-oriented Database
Its architecture uses (a) persistent, sparse matrix, multi-dimensional mapping (row-value, column-value, and timestamp) in a tabular format meant for massive scalability (over and above the petabyte scale).

Source:
- https://stackoverflow.com/questions/62010368/what-exactly-is-a-wide-column-store
- https://www.baeldung.com/cassandra-column-family-data-model
# Ring cluster
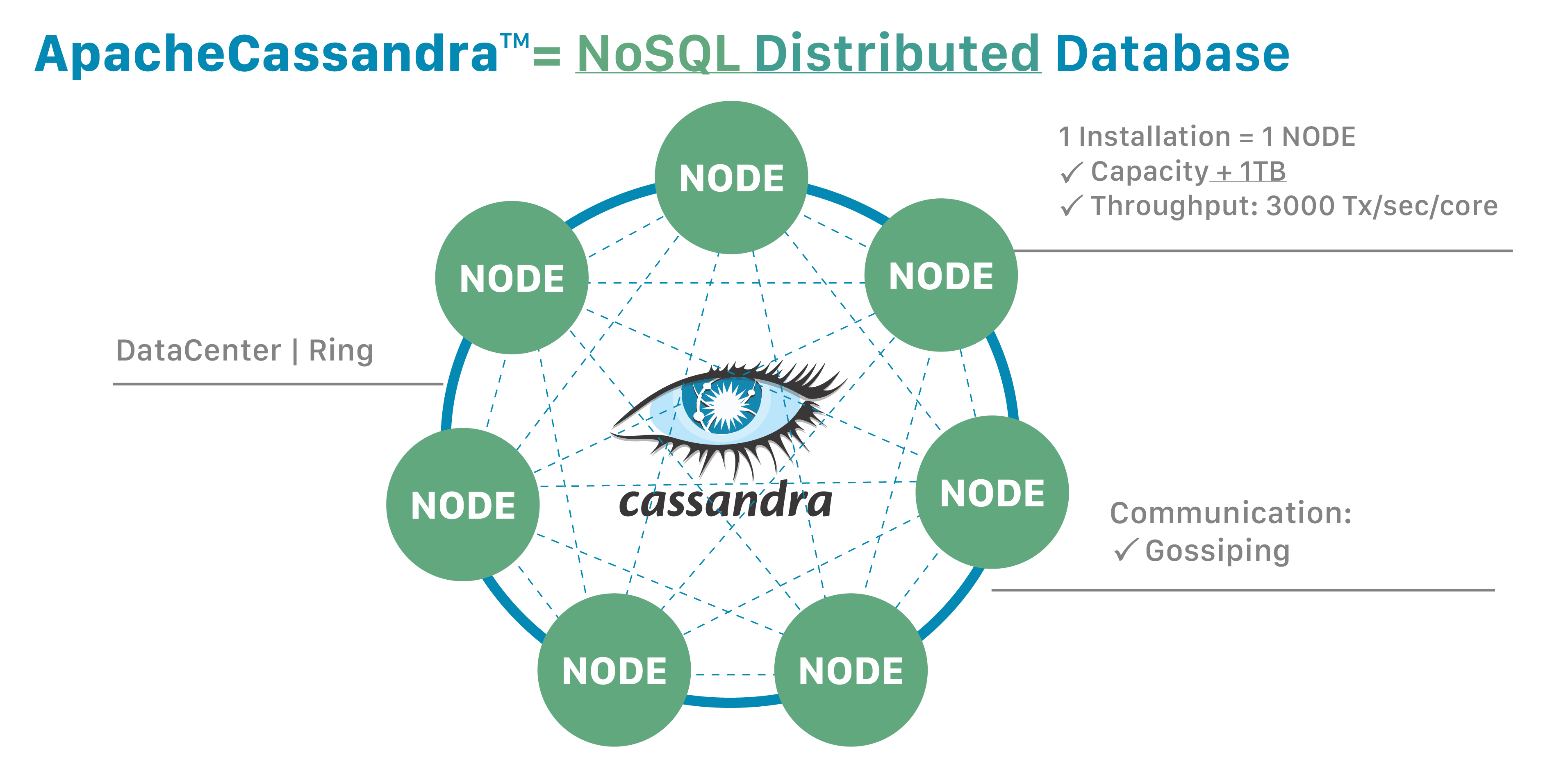
- Each nodes will be assigned a range of token.
- Client could connect any nodes to write, that node will become coordinator node.
- Partition keys will be hashed into a token. Coordinator will base on the token to know which node we can store the data.
- When a Cassandra node becomes unavailable, processing continues and failed writes are temporarily saved as hints on the coordinator. If the hints have not expired, they are applied to the node when it becomes available.
# Replication Factor
- Replication Factor (RF) = number copies we want to store
- Replication node will be defined by Replication Strategy
- Simple strategy = next 2 nodes
# Consistent hashing
... TODO
# Data consistency
| WRITE | READ | Consistent | Read Availability | Write Availability |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| All | All | ✅ | Low | Low |
| Quorum | All | ✅ | Low | Medium |
| ✅ One | All | ✅ | Low | High |
| All | Quorum | ✅ | Medium | Low |
| ✅ Quorum | Quorum | ✅ | Medium | Medium |
| One | Quorum | ❌ | Medium | High |
| ✅ All | One | ✅ | High | Low |
| Quorum | One | ❌ | High | Medium |
| One | One | ❌ | High | High |
# Keys
- Each table requires a unique primary key.
- The first field listed is the partition key, since its hashed value is used to determine the node to store the data.
- If those fields are wrapped in parentheses then the partition key is composite. Otherwise the first field is the partition key.
- Any fields listed after the partition key are called clustering columns. These store data in ascending or descending order within the partition for the fast retrieval of similar values.
- All the fields together are the primary key.
All data has the same partison key will be store at the same node
We should only access data using the partison key
Every node has 256 virtual nodes in default
# CQL
Tables should reflect the queries we are trying to make
# Keyspace
# Table
# Selection
Write time
SELECT car_make, car_model, writetime(car_model)
FROM employee_by_car_make;
Allow filtering
SELECT * FROM employee_by_id
WHERE name = 'John' ALLOW FILTERING;
# Update
Time to live (60seconds), value will be null after the given time.
Use case: token / coupon is only valid in 24hours
UPDATE employee_by_car_make
USING TTL 60
SET car_model='TRUCK'
WHERE car_make'BMW' AND id='2';
# Collections
UPDATE employee_by_id
SET phone = {'123', '321'}
WHERE id = 1
Append
UPDATE employee_by_id
SET phone = phone + {'555', '444'}
WHERE id = 1
Remove
UPDATE employee_by_id
SET phone = phone - {'555'}
WHERE id = 1