# Amazon Elastic File System (EFS)
# Overview
- Uses NFSv4.1 protocol
- Uses security group to control access to EFS
- Compatible with Linux based AMI (not Windows)
- Encryption at rest using KMS
- POSIX file system (~Linux) that has a standard file API
- File system scales automatically, pay-per-use, no capacity planning!
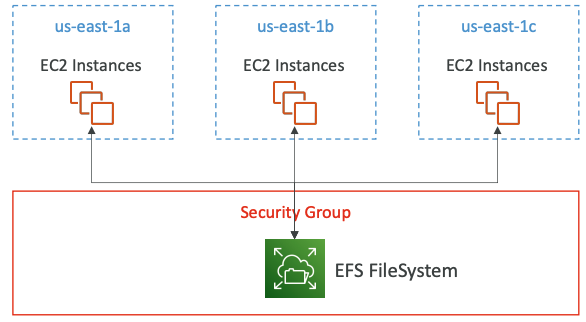
Use cases: content management, web serving, data sharing, Wordpress
# Performance
- EFS Scale
- 1000s of concurrent Network File System (NFS) clients, 10 GB+ /s throughput
- Grow to Petabyte-scale network file system, automatically
- Performance Mode (set at EFS creation time)
- General Purpose (default) – latency-sensitive use cases (web server, CMS, etc…)
- Max I/O – higher latency, throughput, highly parallel (big data, media processing)
- Throughput Mode
- Bursting – 1 TB = 50MiB/s + burst of up to 100MiB/s
- Provisioned – set your throughput regardless of storage size, ex: 1 GiB/s for 1 TB storage
- Elastic – automatically scales throughput up or down based on your workloads
- Up to 3GiB/s for reads and 1GiB/s for writes
- Used for unpredictable workloads
# Storage Classes
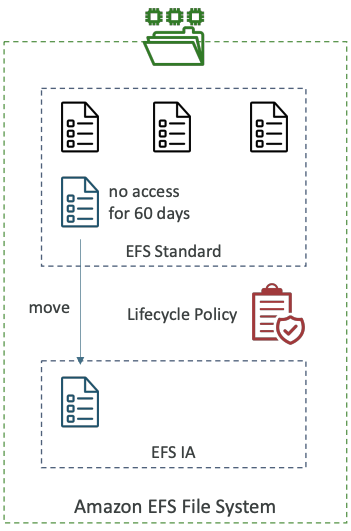
Storage Tiers (lifecycle management feature – move file after N days)
- Standard: for frequently accessed files
- Infrequent access (EFS-IA): cost to retrieve files, lower price to store. Enable EFS -IA with a Lifecycle Policy
Availability and durability
- Standard: Multi-AZ, great for prod
- One Zone: One AZ, great for dev, backup enabled by default, compatible with IA (EFS One Zone-IA)
- Over 90% in cost savings
# EBS vs EFS vs S3
| Category | S3 | EBS | EFS |
|---|---|---|---|
| Storage Type | Object Storage | Block Storage | File Storage |
| Pricing | Pay as you Use | Pay for provisioned capacity | Pay as you Use |
| Storage Size | Unlimited Storage | Limited storage | Unlimited Storage |
| Scalability | Unlimited Scalability | Increase decrease size manually | Unlimited Scalability |
| Durability | Stored redundantly across multiple Azs | Stored redundantly in a Single AZ | Stored redundantly across multiple Azs |
| Availability | Max is 99.99% with S3 Standard | 99.99% | No Service-level agreements (SLAs) |
| Security | Supports Data at Rest & Data in Transit encryption | same | same |
| Back up & Restore | Use Versioning or cross-region replication | Automated Backups and Snapshots | EFS to EFS replication |
| Performace | Slowest | Fastest | Faster than S3, slower than EBS |
| Accessibility | Publicly & privately | only via the attached EC2 instance | simulatenously from multiple EC2 and on-premises instance |
| Interface | Web Interface | File System Interface | Web and File System Interface |
| Use cases | Media, Entertainment, Big data analytics, backups and archives, web serving and content management | Boot volumes, transactional and NoSQL databases, data warehousing ETL | Media, Entertainment, Big data analytics, backups and archives, web serving and content management, home directories |