# Elastic Compute Cloud (EC2)
# Overview
- EC2 is one of the most popular of AWS’ offering
- It mainly consists in the capability of :
- Renting virtual machines (EC2)
- Storing data on virtual drives (EBS)
- Distributing load across machines (ELB)
- Scaling the services using an auto-scaling group (ASG)
- Knowing EC2 is fundamental to understand how the Cloud works
# EC2 sizing & configuration options
- Operating System (OS): Linux, Windows or Mac OS
- How much compute power & cores (CPU)
- How much random-access memory (RAM)
- How much storage space:
- Network-attached (EBS & EFS)
- hardware (EC2 Instance Store)
- Network card: speed of the card, Public IP address
- Firewall rules: security group
- Bootstrap script (configure at first launch): EC2 User Data
# EC2 User Data
- It is possible to bootstrap our instances using an EC2 User data script.
- bootstrapping means launching commands when a machine starts
- That script is only run once at the instance first start
- EC2 user data is used to automate boot tasks such as:
- Installing updates
- Installing software
- Downloading common files from the internet
- Anything you can think of
- The EC2 User Data Script runs with the root user
Example:
#!/bin/bash
# Use this for your user data (script from top to bottom)
# install httpd (Linux 2 version)
yum update -y
yum install -y httpd
systemctl start httpd
systemctl enable httpd
echo "<h1>Hello World from $(hostname -f)</h1>" > /var/www/html/index.html
# EC2 Instance Types
You can use different types of EC2 instances that are optimised for different use cases (opens new window)
Naming convention
AWS has the following naming convention: m5.2xlarge
m: instance class5: generation2xlarge: size within the instance class
# General Purpose
- Great for a diversity of workloads such as web servers or code repositories
- Balance between:
- Compute
- Memory
- Networking
# Compute optimized
Great for compute-intensive tasks that require high performance processors:
- Batch processing workloads
- Media transcoding
- High performance web servers
- High performance computing (HPC)
- Scientific modeling & machine learning
- Dedicated gaming servers
# Memory optimized
Fast performance for workloads that process large data sets in memory
Use cases:
- High performance, relational/non-relational databases
- Distributed web scale cache stores
- In-memory databases optimized for BI (business intelligence)
- Applications performing real-time processing of big unstructured data
# Storage optimized
Great for storage-intensive tasks that require high, sequential read and write access to large data sets on local storage
Use cases:
- High frequency online transaction processing (OLTP) systems
- Relational & NoSQL databases
- Cache for in-memory databases (for example, Redis)
- Data warehousing applications
- Distributed file systems
# Instace types examples
| Instance | vCPU | Mem (GiB) | Storage | Network Performance | EBS Bandwidth (Mbps) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| t2.micro | 1 | 1 | EBS-Only | Low to Moderate | |
| t2.xlarge | 4 | 16 | EBS-Only | Moderate | |
| c5d.4xlarge | 16 | 32 | 1 x 400 NVMe SSD | Up to 10 Gbps | 4,750 |
| r5.16xlarge | 64 | 512 | EBS Only | 20 Gbps | 13,600 |
| m5.8xlarge | 32 | 128 | EBS Only | 10 Gbps | 6,800 |
Full of list ec2 instances.vantage.sh (opens new window)
# Purchasing Options
- On-Demand Instances – short workload, predictable pricing, pay by second
- Reserved (1 & 3 years)
- Reserved Instances – long workloads
- Convertible Reserved Instances – long workloads with flexible instances
- Savings Plans (1 & 3 years) – commitment to an amount of usage, long workload
- Spot Instances – short workloads, cheap, can lose instances (less reliable)
- Dedicated Hosts – book an entire physical server, control instance placement
- Dedicated Instances – no other customers will share your hardware
- Capacity Reservations – reserve capacity in a specific AZ for any duration
# On Demand
- Pay for what you use:
- Linux or Windows - billing per second, after the first minute
- All other operating systems - billing per hour
- Has the highest cost but no upfront payment
- No long-term commitment
- Recommended for short-term and un-interrupted workloads, where you can't predict how the application will behave
# Reserved Instances
- Up to 72% discount compared to On-demand
- You reserve a specific instance attributes (Instance Type, Region, Tenancy, OS)
- Reservation Period – 1 year (+discount) or 3 years (+++discount)
- Payment Options – No Upfront (+), Partial Upfront (++), All Upfront (+++)
- Reserved Instance’s Scope – Regional or Zonal (reserve capacity in an AZ)
- Recommended for steady-state usage applications (think database)
- You can buy and sell in the Reserved Instance Marketplace
- Convertible Reserved Instance
- Can change the EC2 instance type, instance family, OS, scope and tenancy
- Up to 66% discount
# Savings Plans
- Get a discount based on long-term usage (up to 72% - same as RIs)
- Commit to a certain type of usage ($10/hour for 1 or 3 years)
- Usage beyond EC2 Savings Plans is billed at the On-Demand price
- Locked to a specific instance family & AWS region (e.g., M5 in us-east-1)
- Flexible across:
- Instance Size (e.g., m5.xlarge, m5.2xlarge)
- OS (e.g., Linux, Windows)
- Tenancy (Host, Dedicated, Default)
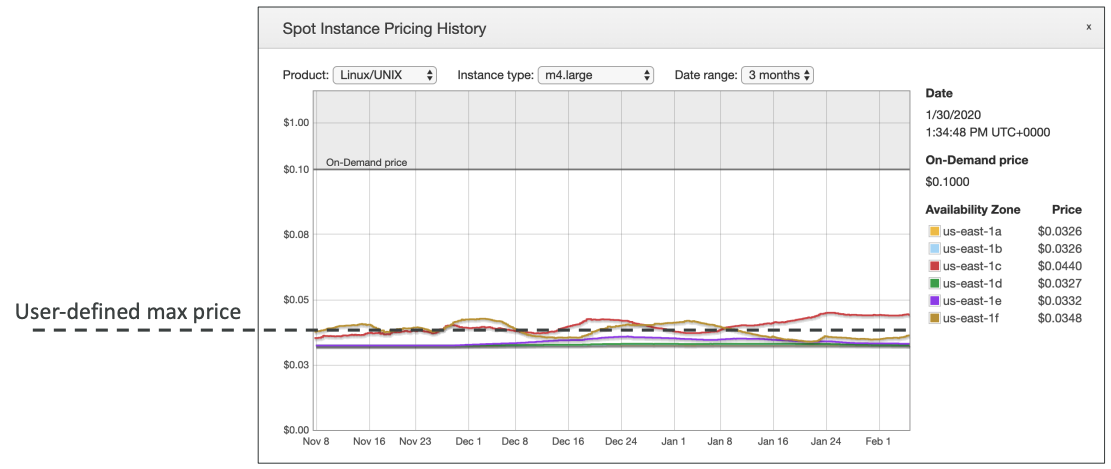
# Spot Instances
- Can get a discount of up to 90% compared to On-demand
- Instances that you can “lose” at any point of time if your max price is less than the current spot price
- The MOST cost-efficient instances in AWS
- Useful for workloads that are resilient to failure
- Batch jobs
- Data analysis
- Image processing
- Any distributed workloads
- Workloads with a flexible start and end time (resilient to failures)
- Not suitable for critical jobs or databases
# Spot Instances Requests
- Define max spot price and get the instance while current spot price < max
- The hourly spot price varies based on offer and capacity
- If the current spot price > your max price you can choose to stop or terminate your instance with a 2 minutes grace period.
- Other strategy: Spot Block (
NO SUPPORT ANYMORE)- “block” spot instance during a specified time frame (1 to 6 hours) without interruptions
- In rare situations, the instance may be reclaimed
Detail link (opens new window)
# Terminate Sspot instances
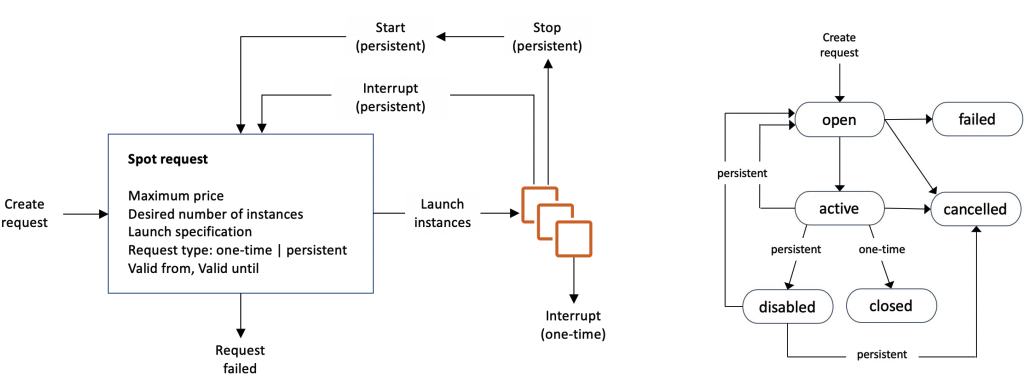
- You can only cancel Spot Instance requests that are open, active, or disabled.
- Cancelling a Spot Request does not terminate instances
- You must first cancel a Spot Request, and then terminate the associated Spot Instances
# Spot fleets
- Spot Fleets = set of Spot Instances + (optional) On-Demand Instances
- The Spot Fleet will try to meet the target capacity with price constraints
- Define possible launch pools: instance type (m5.large), OS, Availability Zone
- Can have multiple launch pools, so that the fleet can choose
- Spot Fleet stops launching instances when reaching capacity or max cost
- Strategies to allocate Spot Instances:
- lowestPrice: from the pool with the lowest price (cost optimization, short workload)
- diversified: distributed across all pools (great for availability, long workloads)
- capacityOptimized: pool with the optimal capacity for the number of instances
- priceCapacityOptimized (recommended): pools with highest capacity available, then select the pool with the lowest price (best choice for most workloads)
- Spot Fleets allow us to automatically request Spot Instances with the lowest price
# Dedicated Hosts
- A physical server with EC2 instance capacity fully dedicated to your use
- Allows you address compliance requirements and use your existing server- bound software licenses (per-socket, per-core, pe—VM software licenses)
- Purchasing Options:
- On-demand – pay per second for active Dedicated Host
- Reserved - 1 or 3 years (No Upfront, Partial Upfront, All Upfront)
- The most expensive option
- Useful for software that have complicated licensing model (BYOL – Bring Your Own License)
- Or for companies that have strong regulatory or compliance needs
# Dedicated Instances
- Instances run on hardware that’s dedicated to you
- May share hardware with other instances in same account
- No control over instance placement (can move hardware after Stop / Start)
| Characteristic | Dedicated Instances | Dedicated Hosts |
|---|---|---|
| Enables the use of dedicated physical servers | ✅ | ✅ |
| Per instance billing (subject to a $2 per region fee) | ✅ | |
| Per host billing | ✅ | |
| Visibility of sockets, cores, host ID | ✅ | |
| Affinity between a host and instance | ✅ | |
| Targeted instance placement | ✅ | |
| Automatic instance placement | ✅ | ✅ |
| Add capacity using an allocation request | ✅ |
# Capacity Reservations
- Reserve On-Demand instances capacity in a specific AZ for any duration
- You always have access to EC2 capacity when you need it
- No time commitment (create/cancel anytime), no billing discounts
- Combine with Regional Reserved Instances and Savings Plans to benefit from billing discounts
- You’re charged at On-Demand rate whether you run instances or not
- Suitable for short-term, uninterrupted workloads that needs to be in a specific AZ
# Which option is right for me?
- On demand: coming and staying in resort whenever we like, we pay the full price
- Reserved: like planning ahead and if we plan to stay for a long time, we may get a good discount.
- Savings Plans: pay a certain amount per hour for certain period and stay in any room type (e.g., King, Suite, Sea View, …)
- Spot instances: the hotel allows people to bid for the empty rooms and the highest bidder keeps the rooms. You can get kicked out at any time
- Dedicated Hosts: We book an entire building of the resort
- Capacity Reservations: you book a room for a period with full price even you don’t stay in it
# Price Comparison
Example – m4.large – us-east-1
| Price | Type Price (per hour) |
|---|---|
| On-Demand | $0.10 |
| Spot Instance (Spot Price) | $0.038 - $0.039 (up to 61% off) |
| Reserved Instance (1 year) | $0.062 (No Upfront) - $0.058 (All Upfront) |
| Reserved Instance (3 years) | $0.043 (No Upfront) - $0.037 (All Upfront) |
| EC2 Savings Plan (1 year) | $0.062 (No Upfront) - $0.058 (All Upfront) |
| Reserved Convertible Instance (1 year) | $0.071 (No Upfront) - $0.066 (All Upfront) |
| Dedicated Host | On-Demand Price |
| Dedicated Host Reservation | Up to 70% off |
| Capacity Reservations | On-Demand Price |
# Placement Groups
- Sometimes you want control over the EC2 Instance placement strategy
- That strategy can be defined using placement groups
- When you create a placement group, you specify one of the following strategies for the group:
- Cluster—clusters instances into a low-latency group in a single Availability Zone
- Spread—spreads instances across underlying hardware (max 7 instances per group per AZ)
- Partition—spreads instances across many different partitions (which rely on different sets of racks) within an AZ. Scales to 100s of EC2 instances per group (Hadoop, Cassandra, Kafka)
# Placement Groups Cluster
- ✅ Pros: Great network (10 Gbps bandwidth between instances with Enhanced Networking enabled - recommended)
- ❌ Cons: If the rack fails, all instances fails at the same time
Use case:
- Big Data job that needs to complete fast
- Application that needs extremely low latency and high network throughput
# Placement Groups Spread
- ✅ Pros:
- Can span across Availability Zones (AZ)
- Reduced risk is simultaneous failure
- EC2 Instances are on different physical hardware
- ❌ Cons: Limited to 7 instances per AZ per placement group
Use case:
- Application that needs to maximize high availability
- Critical Applications where each instance must be isolated from failure from each other
# Placement Groups Partition
placement group Partition each partition represent a rack in AWS
- Up to 7 partitions per AZ
- Can span across multiple AZs in the same region
- Up to 100s of EC2 instances
- The instances in a partition do not share racks with the instances in the other partitions
- A partition failure can affect many EC2 but won’t affect other partitions
- EC2 instances get access to the partition information as metadata
Use case: HDFS, HBase, Cassandra, Kafka
# Hibernate
We know we can stop, terminate instances
- Stop – the data on disk (EBS) is kept intact in the next start
- Terminate – any EBS volumes (root) also set-up to be destroyed is lost
On start, the following happens:
- First start: the OS boots & the EC2 User Data script is run
- Following starts: the OS boots up
- Then your application starts, caches get warmed up, and that can take time!
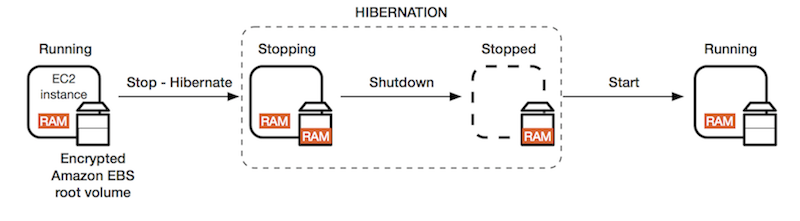
# Overview
- The in-memory (RAM) state is preserved
- The instance boot is much faster! (the OS is not stopped / restarted)
- Under the hood: the RAM state is written to a file in the root EBS volume
- The root EBS volume must be encrypted
Use cases:
- Long-running processing
- Saving the RAM state
- Services that take time to initialize
# Good to know
- Supported Instance Families – C3, C4, C5, I3, M3, M4, R3, R4, T2, T3, …
- Instance RAM Size – must be less than 150 GB.
- Instance Size – not supported for bare metal instances.
- AMI – Amazon Linux 2, Linux AMI, Ubuntu, RHEL, CentOS & Windows…
- Root Volume – must be EBS, encrypted, not instance store, and large
- Available for On-Demand, Reserved and Spot Instances
- An instance can NOT be hibernated more than 60 days
# EC2 Instance Store
- Provide temporary block level storage for instance.
- The storage is a disk that physically attached to host.
- Good for buffer / cache / scratch data / temporary content
- Ideal workload: buffers, caches, scratch data, temporary content
- Data is lost when:
- Underlying disk drive fails
- Instance stop / hibernates / terminates
- Backups and Replication are your responsibility
- Very high IOPS: up to million IOPS (Eg: i3.16xlarge 3.3M read and 1.4M write IOPS). If you need a high-performance hardware disk, use EC2 Instance Store
Ref: Better I/O performance (opens new window)
# Amazon Machine Image (AMI)
- AMI are a customization of an EC2 instance
- You add your own software, configuration, operating system, monitoring…
- Faster boot / configuration time because all your software is pre-packaged
- AMI are built for a specific region (and can be copied across regions)
- You can launch EC2 instances from:
- A Public AMI: AWS provided
- Your own AMI: you make and maintain them yourself
- An AWS Marketplace AMI: an AMI someone else made (and potentially sells)
# AMI Process (from an EC2 instance)
- Start an EC2 instance and customize it
- Stop the instance (for data integrity)
- Build an AMI – this will also create EBS snapshots
- Launch instances from other AMIs