# Kubernetes (K8S) notes

# Architecture

https://xuanthulab.net/kubernetes/
# Control Plane
The Control Plane or (Master Node) controls your K8s cluster, and it consists of multiple components that are responsible of managing that cluster. Usually, all the components are installed on the same machine for simplicity, but of course control plane components can be distributed among machines within the cluster. The main components that form K8s and are related to your control plane are:
- kube-api-server: Interacting with K8s cluster is done through the kube-api-serer which is the primary interface to the control plane and the cluster.
- etcd: A key-value store that K8s uses as its data store for the cluster. It is high available and reliable storage for fast data access and retrieval.
- kube-scheduler: When creating and running containers, kube-scheduler makes sure to select the right available node to run the container.
- kube-controller-manager: Contains multiple logical controllers that handle the state of K8s objects. Some of those controllers are node-controller, job-controller, and service-account-controller.
- cloud-controller-manager: Provides an interface between K8s and different cloud platforms. It’s only used when using cloud-based resources alongside K8s.
# Nodes
One or more nodes can be installed, whether it be on a virtual or physical machine, depending on the cluster. Each node is managed by the control plane, and contains the necessary services to run pods and communicate directly with the control plane. These are made up of:
- kubelet: An agent that runs on each node––it communicates with the control plane to ensure that the containers run on the node as required by the control plane. Also, it reports back the state of the running containers to the control plane.
- kube-proxy: A network proxy that runs on each node and that handles network rules on nodes. These network rules allow network communication between your Pods, from network sessions inside or outside of your cluster.
- container runtime: The container runtime is the software that is responsible for running containers: you need to install a container runtime in each node within the cluster so that Pods can run there. K8s supports several container runtimes, the most popular of which are Docker & containerd.
# Resource types
In Kubernetes, resource types are the building blocks that define the various components and objects that can be managed within a cluster. Each resource type represents a specific kind of object that can be created, updated, or deleted in a Kubernetes cluster.
Kubernetes provides a wide range of resource types to cater to different requirements and functionalities. Some common resource types include:
Pods: Pods are the smallest and most basic unit in Kubernetes. They represent a single instance of a running process in a cluster.
Deployments: Deployments are used to manage the lifecycle of a set of pods. They provide declarative updates for pods and their associated resources, such as replica sets.
Services: Services enable communication between different pods and external clients. They provide a stable network endpoint for accessing a set of pods.
ReplicaSets: ReplicaSets are used to ensure a specified number of pod replicas are running at all times. They are the underlying mechanism behind deployments and provide scaling and self-healing capabilities.
StatefulSets: StatefulSets are used to manage stateful applications that require stable network identities and persistent storage. They provide guarantees for ordering and uniqueness of pod names, as well as stable network identities and persistent storage volumes.
ConfigMaps: onfigMaps are used to store configuration data that can be consumed by pods. They allow you to decouple configuration from your application code and provide a way to manage configuration changes without redeploying your application.
Secrets: Secrets are similar to ConfigMaps but are specifically designed for storing sensitive information, such as passwords or API keys, that should not be exposed in plain text. They are similar to ConfigMaps but provide encryption and additional security features. They are base64-encoded and can be mounted as files or used as environment variables in pods.
Persistent Volumes: PersistentVolumes (PVs) are used to provide persistent storage for stateful applications. They represent a piece of network-attached storage in the cluster and can be dynamically provisioned or statically defined.
PersistentVolumeClaims: PersistentVolumeClaims (PVCs) are used to request storage resources from PersistentVolumes. They provide a way for applications to dynamically request and bind to available storage resources.
Namespaces: Namespaces are used to create virtual clusters within a physical Kubernetes cluster. They provide a way to divide cluster resources between multiple users or teams.
# Pod

Kubernetes không chạy các container một cách trực tiếp, thay vào đó nó bọc một hoặc vài container vào với nhau trong một cấu trúc gọi là POD. Các container cùng một pod thì chia sẻ với nhau tài nguyên và mạng cục bộ của pod.
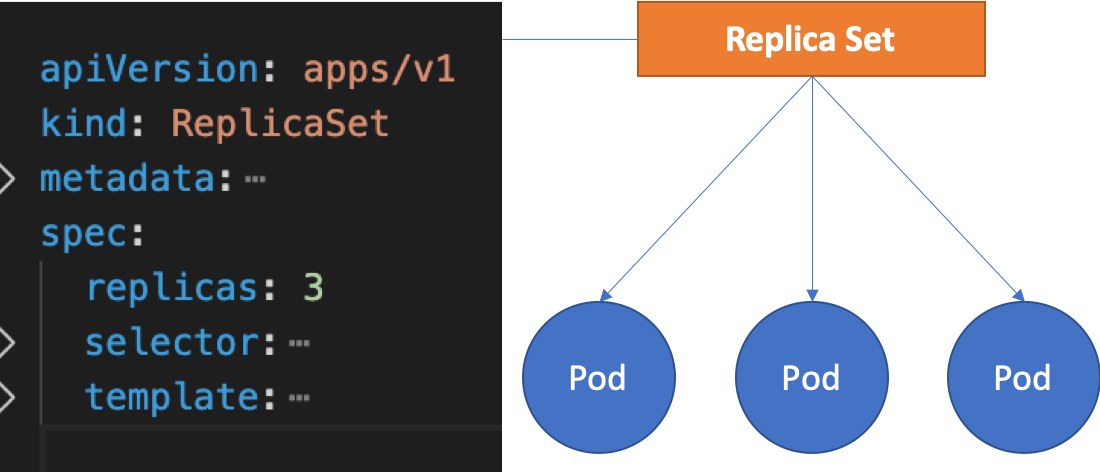
# ReplicaSet

ReplicaSet là một điều khiển Controller - nó đảm bảo ổn định các nhân bản (số lượng và tình trạng của POD, replica) khi đang chạy.
# HorizontalPodAutoscaler (HPA)
Horizontal Pod Autoscaler là chế độ tự động scale (nhân bản POD) dựa vào mức độ hoạt động của CPU đối với POD, nếu một POD quá tải - nó có thể nhân bản thêm POD khác và ngược lại - số nhân bản dao động trong khoảng min, max cấu hình
# Deployment

Deployment quản lý một nhóm các Pod - các Pod được nhân bản, nó tự động thay thế các Pod bị lỗi, không phản hồi bằng pod mới nó tạo ra. Như vậy, deployment đảm bảo ứng dụng của bạn có một (hay nhiều) Pod để phục vụ các yêu cầu.
Deployment sử dụng mẫu Pod (Pod template - chứa định nghĩa / thiết lập về Pod) để tạo các Pod (các nhân bản replica), khi template này thay đổi, các Pod mới sẽ được tạo để thay thế Pod cũ ngay lập tức.
# Service

Service (micro-service) là một đối tượng trừu tượng nó xác định ra một nhóm các POD và chính sách để truy cập đến POD đó. Nhóm cá POD mà Service xác định thường dùng kỹ thuật Selector (chọn các POD thuộc về Service theo label của POD).
Cũng có thể hiểu Service là một dịch vụ mạng, tạo cơ chế cân bằng tải (load balancing) truy cập đến các điểm cuối (thường là các Pod) mà Service đó phục vụ.
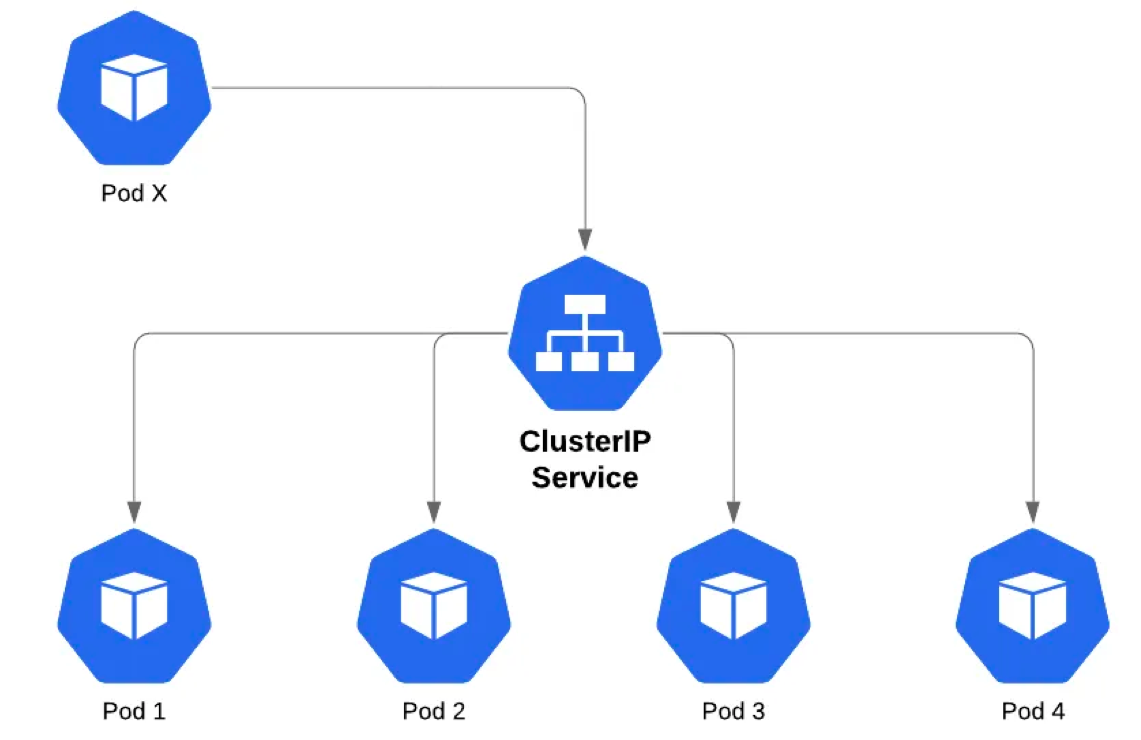
Các POD được quản lý trong Kubernetes, trong vòng đời của nó chỉ diễn ra theo hướng - được tạo ra, chạy và khi nó kết thúc thì bị xóa và khởi tạo POD mới thay thế. ! Có nghĩa ta không thể có tạm dừng POD, chạy lại POD đang dừng ...
Mặc dù mỗi POD khi tạo ra nó có một IP để liên lạc, tuy nhiên vấn đề là mỗi khi POD thay thế thì là một IP khác, nên các dịch vụ truy cập không biết IP mới nếu ta cấu hình nó truy cập đến POD nào đó cố định. Để giải quết vấn đề này sẽ cần đến Service.
# Service types

# Headless Service
Các Service trên có một địa chỉ IP riêng của Service, nó dùng cơ chế cân bằng tải để liên kết với các POD. Tuy nhiên nếu nuốn không dùng cơ chế cân bằng tải, mỗi lần truy cập tên Service nó truy cập thẳng tới IP của PO thì dùng loại Headless Service.
Một Headless Service (Service không IP) nó liên kết thẳng với IP của POD, có nghĩa bạn sẽ không tương tác trực tiếp với POD qua proxy.
# Namespace

- dev-ns
- prod-ns
Namespaces are used to create virtual clusters within a physical Kubernetes cluster. They provide a way to divide cluster resources between multiple users or teams.
# Ingress
Ingress là thành phần được dùng để điều hướng các yêu cầu traffic giao thức HTTP và HTTPS từ bên ngoài (interneet) vào các dịch vụ bên trong Cluster.
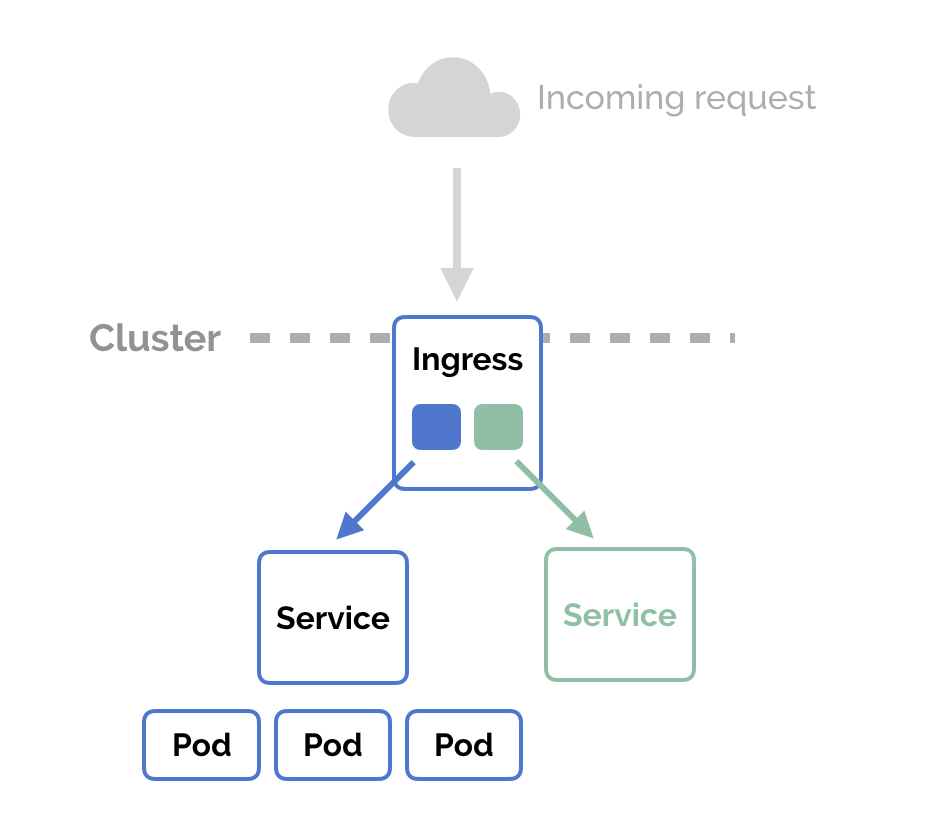
Ingress chỉ để phục vụ các cổng, yêu cầu HTTP, HTTPS còn các loại cổng khác, giao thức khác để truy cập được từ bên ngoài thì dùng Service với kiểu NodePort và LoadBalancer
Để Ingress hoặt động, hệ thồng cần một điều khiển ingress trước (Ingress controller), có nhiều loại để chọn sử dụng (tham khảo Ingress Controller)
Nếu chọn Ngix Ingress Controller thì cài đặt theo: NGINX Ingress Controller for Kubernetes.
Phần này, chọn loại HAProxy Ingress Controller - HAProxy Ingress Controller
# Others
# DaemonSet
DaemonSet (ds) đảm bảo chạy trên mỗi NODE một bản copy của POD. Triển khai DaemonSet khi cần ở mỗi máy (Node) một POD, thường dùng cho các ứng dụng như thu thập log, tạo ổ đĩa trên mỗi Node .
# Job
Job có chức năng tạo các POD đảm bảo nó chạy và kết thúc thành công. Khi các POD do Job tạo ra chạy và kết thúc thành công thì Job đó hoàn thành. Khi bạn xóa Job thì các Pod nó tạo cũng xóa theo. Một Job có thể tạo các Pod chạy tuần tự hoặc song song. Sử dụng Job khi muốn thi hành một vài chức năng hoàn thành xong thì dừng lại (ví dụ backup, kiểm tra ...) Khi Job tạo Pod, Pod chưa hoàn thành nếu Pod bị xóa, lỗi Node ... nó sẽ thực hiện tạo Pod khác để thi hành tác vụ.
# CronJob
CronJob (cj) - chạy các Job theo một lịch định sẵn. Việc lên lịch cho CronJob khai báo giống Cron của Linux.
# Persistent Volume (pv) & PersistentVolumeClaim (pvc)
PersistentVolume (pv) là một phần không gian lưu trữ dữ liệu trong cluster, các PersistentVolume giống với Volume bình thường tuy nhiên nó tồn tại độc lập với POD (pod bị xóa PV vẫn tồn tại), có nhiều loại PersistentVolume có thể triển khai như NFS, Clusterfs
PersistentVolumeClaim (pvc) là yêu cầu sử dụng không gian lưu trữ (sử dụng PV). Hình dung PV giống như Node, PVC giống như POD. POD chạy nó sử dụng các tài nguyên của NODE, PVC hoạt động nó sử dụng tài nguyên của PV.
https://stackoverflow.com/questions/45079988/ingress-vs-load-balancer
https://jlvbcoop.com/en/eventbus-kubernetes/
# K8S kubectl commands

# Design patterns
# Patterns Overview

# Top Patterns


https://developers.redhat.com/blog/2020/05/11/top-10-must-know-kubernetes-design-patterns#behavioral_patterns
# Scaling patterns

# On cloud
# EKS

# Ecosystem
