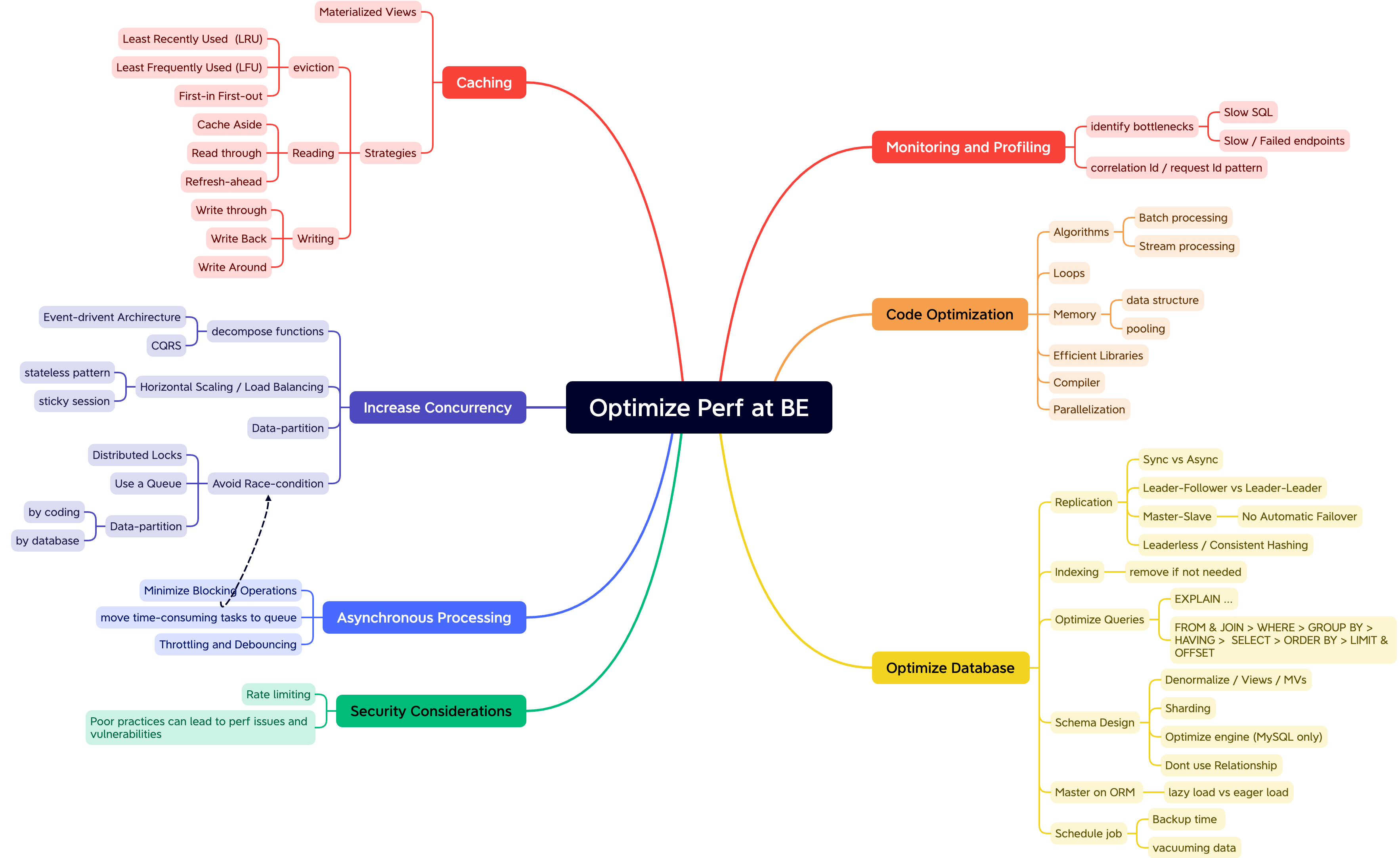
# Optimize Performance at Backend
# Reducing the time response, cope to load
- increase the resource
- vertial scaling
- horizotal scaling
- store user data at global storage
- session data
- uploading files
- store user data at global storage
- partially, put the long-processing task in to the queue
- re-design / re-architect
- message queues & events
- graceful service
# Increase concurrency
- Optimize code performance
- Scale-out
- Cloning to multiple processes (X-Axis) (Stateless pattern, Replica In DB)
- Splitting by functions (Y-Axis) (Domain Driven pattern)
- Data partitioning (Z-Axis) (Sharding)
# Race condition
Solutions:
- Distributed locks
- Data sharding
- Use a queue - multiple consumers (balancing)
# Materialized View - CQRS
- Caching layer
- turning database inside-out / building the materialized view
- Read model have a high-speed for reading
# Code Optimization
ode optimization is a crucial step in software development that aims to improve the performance and efficiency of a program. By optimizing code, developers can reduce execution time, minimize resource usage, and enhance overall user experience. In this article, we will explore some effective techniques for code optimization.
# Algorithmic Optimization
One of the most fundamental ways to optimize code is by improving the underlying algorithms. Analyze the algorithms used in your code and look for opportunities to make them more efficient. Consider alternative algorithms or data structures that can achieve the same result with fewer operations or reduced memory usage. By choosing the right algorithm, you can significantly improve the performance of your code.
# Loop Optimization
Loops are often a major source of performance bottlenecks. To optimize loops, consider the following techniques:
- Reduce the number of iterations: Analyze the loop conditions and break out of the loop as soon as the desired result is achieved.
- Minimize function calls within loops: Move function calls outside the loop or inline them to avoid unnecessary overhead.
- Use loop unrolling: Unroll loops by manually duplicating loop bodies to reduce loop overhead and improve cache utilization.
# Original loop
sum = 0
for i in range(1, 1001):
sum += i
# Optimized loop
n = 1000
sum = (n * (n + 1)) // 2
# Memory Optimization
Efficient memory usage is crucial for code optimization. Consider the following techniques to optimize memory:
- Minimize memory allocations: Reduce the number of dynamic memory allocations by reusing objects or using static memory where possible.
- Optimize data structures: Choose data structures that are optimized for memory access patterns and minimize memory fragmentation.
- Use memory pooling: Implement memory pooling techniques to reuse memory blocks instead of allocating and deallocating them repeatedly.
# Compiler Optimization
Modern compilers offer various optimization options that can significantly improve code performance. Enable compiler optimizations, such as loop unrolling, inlining, and constant propagation. Additionally, use compiler-specific flags and directives to guide the optimization process.
# Profiling and Benchmarking
Profiling and benchmarking tools help identify performance bottlenecks in your code. Use these tools to measure the execution time of different code sections and identify areas that require optimization. Focus on optimizing the critical sections of your code that consume the most resources or have the highest impact on overall performance.
# Parallelization
Parallelizing code can greatly improve performance, especially on multi-core processors. Identify sections of your code that can be executed concurrently and utilize parallel programming techniques, such as multithreading or multiprocessing, to distribute the workload across multiple cores.
# Use Efficient Libraries and APIs
Leverage efficient libraries and APIs that are specifically designed for performance-critical tasks. These libraries are often highly optimized and can provide significant performance improvements over custom implementations.
# Code Proficiency
Improving your coding skills and proficiency can also lead to better code optimization. Stay updated with the latest programming techniques, design patterns, and best practices. Write clean, modular, and maintainable code that is easier to optimize and understand.
# Optimization Database
- scalable architecture
- master - replica
- partioning data: horizontal & vertial
- optimize the query
- ORM usage : lazy vs eager
- indexing database
- use cursor instead of loop
- transaction lock rows
- pessimistic locking
- optimistic locking
- views
WARNING
CAP Theorem: Tradeoff between Availability vs Consistency
# Optimized Network
When dealing with async processing that involves network communication, optimizing the network layer can have a significant impact on performance. Techniques like connection pooling, compression, and caching at the network level can reduce latency and improve overall throughput.
# Minimize Round Trips
Reducing the number of round trips between the client and server is one of the most effective ways to optimize network communication. Each round trip introduces latency and overhead, so it's important to minimize them. Here are a few strategies to achieve this:
- Batching Requests: Instead of sending multiple small requests, combine them into a single larger request. This reduces the number of round trips and improves efficiency.
- Caching: Implement client-side caching to store frequently accessed data. This reduces the need for network requests and improves response times.
- Compression: Compress data before sending it over the network. This reduces the amount of data transferred, resulting in faster communication.
# Use Efficient Protocols
Choosing the right network protocol can significantly impact performance. Consider the following:
- HTTP/2: If you're using HTTP, consider upgrading to HTTP/2. It introduces features like multiplexing, server push, and header compression, which can greatly improve network performance.
- WebSockets: For real-time communication, consider using WebSockets instead of traditional HTTP requests. WebSockets provide a persistent connection, reducing the overhead of establishing new connections for each request.
# Optimize Data Transfer
Efficiently transferring data over the network is essential for optimal performance. Here are a few techniques to consider:
- Data Compression: Compress data using algorithms like GZIP or Brotli. This reduces the size of the data being transferred, resulting in faster communication.
- Data Pagination: When dealing with large datasets, implement pagination to retrieve data in smaller chunks. This reduces the amount of data transferred in each request.
- Data Serialization: Choose a compact and efficient data serialization format, such as JSON or Protocol Buffers. This reduces the size of the data being transferred and improves performance.
# Monitor
Regularly monitoring network performance is crucial for identifying bottlenecks and areas for improvement. Consider the following:
- Network Profiling: Use network profiling tools to analyze network traffic and identify performance bottlenecks. This can help pinpoint areas that require optimization.
- Latency Analysis: Measure and analyze network latency to identify potential areas for improvement. Reduce latency by optimizing server response times and minimizing network congestion.
- Load Testing: Perform load testing to simulate real-world scenarios and identify performance limitations. This helps optimize network communication for high traffic situations.
# Tools
- Timers
- Code analyzers (IDE, DB Profiling)
- Debugger
- Logging
- Efficient Code (runtime, memmory alloc)
# Comparision
- goroutines vs worker threads P1 (opens new window)
- goroutines vs worker threads P2 (opens new window)