# Object oriented programming (OOP) Notes
Vietsub: Lập trình hướng đối tượng
- OOP là một kỹ thuật lập trình cho phép lập trình viên
tạo ra các đối tượngtrong code đểtrừu tượng hóacác đối tượng thực tế trong cuộc sống.
# ✅ 4 tính chất
# Encapsulation - Tính đóng gói
- Che dấu những tính chất xử lý bên trong của đối tượng giống như nội tâm của 1 con người vậy đó =))
- Thể hiện qua các
propertyhoặcmethodprivate
# Inheritance - Tính kế thừa
- Cho phép kế thừa lại những tính năng mà một đối tượng khác đã có
- Những thứ nằm ở private thì sẽ ko được thừa kế ^^!
- Những thứ protected - chỉ có những người trong dòng tộc mới có thể sử dụng được
- Thể hiện qua keywords: extends hoặc implements
# Polymorphism - Tính đa hình
Một tác vụ được thực hiện theo nhiều cách khác nhau được gọi là tính đa hình. Thể hiện qua Overloading và Overriding:
- Overloading: các method có cùng tên nhưng khác tham số
- Overriding: ghi đè lại các method của một lớp cha
Polymorphic is typically implemented as either of following:
- Tables for all method calls prepared statically (as in C++ & Java)
- A method lookup at each call (Javascript & Python)
Note:
- PHP không có
Overloading...
# Abstraction - Tính trừu tượng
- Một tiến trình ẩn các chi tiết trình triển khai và chỉ hiển thị tính năng tới người dùng
- Được thể hiện qua abstract class và các interface`
# ✅ Mối quan hệ
Dưới đây là 1 số mối quan hệ giữa các class với nhau
# Inheritance
- Quan hệ cha con ruột thịt là đây, kế thừa lại những tính năng mà một đối tượng khác đã có
# Aggregation
- là mối quan hệ has-a.
- Class A có quan hệ
Aggregationvới class B khi class A có method dùng B như parameter - Vòng đời độc lập với nhau
class A {
void doXXX (B b) { };
};
# Composition
- Đây là 1 dạng quan hệ Aggregation nhưng ở dạng strong type
- Class A có quan hệ
Compostionvới class B khi constructor của class A dùng B như parameter. - Khi Instance A được khởi tạo thì instance B cũng được khởi tạo, chúng tồn tại và bị hủy đồng thời
class A {
A () {
new B ();
}
};
# Association
- Cũng thể hiện quan hệ giữa hai đối tượng. Mỗi đối tượng đểu có life cycle riêng và không có mối quan hệ kiểu owner
- Associate giữa hai đối tượng được khởi tạo qua reference properties (class attributes)
- Class A có quan hệ Associate với class B tức là 1 class A có member có kiểu class B
class A {
private B b;
};
# OOAD
# Phases
- Object–Oriented Analysis
- Object–Oriented Design
- System Design
- Object Design
- Object–Oriented Implementation and Testing
# OO Analysis
# Object Modelling
Object modelling develops the static structure of the software system in terms of objects.
- Identify objects and group into classes
- Identify the relationships among classes
- Create user object model diagram
- Define user object attributes
- Define the operations that should be performed on the classes
- Review glossary
# Dynamic Modelling
After the static behavior of the system is analyzed, its behavior with respect to time and external changes needs to be examined.
- Identify states of each object
- Identify events and analyze the applicability of actions
- Construct dynamic model diagram, comprising of state transition diagrams
- Express each state in terms of object attributes
- Validate the state–transition diagrams drawn
# Functional Modelling
The functional model shows the processes that are performed within an object and how the data changes as it moves between methods.
- Identify all the inputs and outputs
- Construct data flow diagrams showing functional dependencies
- State the purpose of each function
- Identify constraints
- Specify optimization criteria
# ✅ Design Pattern
Design pattern mô tả một giải pháp được thiết lập cho các vấn đè thường gặp nhất trong thiết kế phần mềm
Giang hồ truyền miệng nhau có 3 loại chính: Creational, Structural, Behavioral
Dưới đây là 2 trang web mình hay dùng để tham khảo 😃) Có phải thần đồng hay siêu năng lực gì đâu mà nhớ được hết
Sau khi xem qua sơ 2 web trên đó, bạn có thể nhận thấy họ vẽ các cơ số hình học, ký hiệu lạ lùng để miêu tả quan hệ cũng như phương thức của các class. Yup, đó là UML.
# ✅ Unified Modeling Language (UML)
Vietsub: (Theo wiki) Ngôn ngữ mô hình hóa thống nhất =))
UML là một ngôn ngữ mô hình gồm các ký hiệu đồ họa mà các phương pháp hướng đối tượng sử dụng để thiết kế các hệ thống thông tin một cách nhanh chóng.
Cho tấm hình nghiền ngẫm chứ chả biết nói gì thêm :p
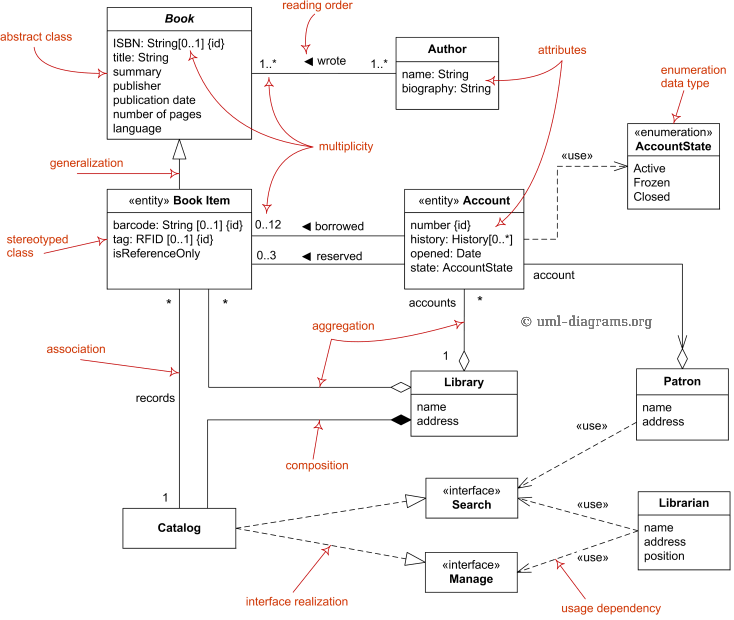
# ✅ SOLID Principles
SOLID là viết tắt của 5 chữ cái đầu trong 5 nguyên tắc thiết kế hướng đối tượng
# Single responsibility priciple (SRP)
An active corollary to Conway’s law:
TIP
The best structure for a software system is heavily influenced by the social structure of the organization that uses it so that each software module has one, and only one, reason to change.
# Open/Closed principle (OCP)
Bertrand Meyer made this principle famous in the 1980s.
TIP
The gist is that for software systems to be easy to change, they must be designed to allow the behavior of those systems to be changed by adding new code, rather than changing existing code (open for extension but closed for modification).
# Liskov substitution principe (LSP)
Barbara Liskov’s famous definition of subtypes, from 1988.
TIP
In short, this principle says that to build software systems from interchangeable parts, those parts must adhere to a contract that allows those parts to be substituted one for another.
# Interface segregation principle (ISP)
TIP
This principle advises software designers to avoid depending on things that they don’t use.
Thay vì dùng 1 interface lớn, ta nên tách thành nhiều interface nhỏ, với nhiều mục đích cụ thể
# Dependency inversion principle (DIP)
TIP
The code that implements high-level policy should not depend on the code that implements low-level details. Rather, details should depend on policies.
Interface (abstraction) không nên phụ thuộc vào chi tiết, mà ngược lại. ( Các class giao tiếp với nhau thông qua interface, không phải thông qua implementation.)
# note nhẹ
- Trong 1 App thì có nhiều Class
- 1 Class thì có nhiều
instance(đối tượngcó thể gọi làcá thể) - Một instance thì có
property(thuộc tính) vàmethod(phương thức)
# Concrete class
Bên cạnh Abstract class là class ko thể khởi tạo trực tiếp thì ngược lại với nó là Concrete class